Urinary System
Abnormal Urine Output
| Term | Definition (mL/kg/h) | Definition (mL/d) |
|---|---|---|
| Polyuria | > 1.5 mL/kg/h | > 2000 mL/d |
| Normal | 0.5 ~ 1.5 mL/kg/h | 800 ~ 2000 mL/d |
| Oliguria | < 0.5 mL/kg/h | < 500 mL/d |
| Anuria | 0 mL/kg/h | < 100 mL/d |
Abnormal Urine Color
| Color | Diseases |
|---|---|
| Orange | Rifampin |
| Black | Alkaptonuria |
| Red | Hematuria Hemoglobinuria Myoglobinuria |
| Brown | Hyperbilirubinemia |
| Purple | Porphyria |
Abnormal Microscopic Findings in Urine
| Finding | Contents | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| RBC casts | RBCs | Glomerulonephritis |
| WBC casts | WBCs | UTI Glomerulonephritis Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) |
| RTE cell casts | RTE cells | Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) |
| Hyaline casts | Mucoprotein | - |
| Granular casts | Cellular debris | Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) |
| Waxy casts | Cellular debris | Chronic kidney disease (CKD) |
| Fatty casts | Lipids | Nephrosis |
| Envelope crystals | Calcium oxalate | Ethylene glycol Malabsorption |
| Coffin lid crystals | Struvite | Urease-positive pathogens |
| Rhomboid crystals | Uric acid | Hyperuricemia |
| Hexagonal crystals | Cystine | Cystinuria |
Diuretics
| Mechanism | Mnemonic | Medication | Location | K | H | Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors | Abnormal | Acetazolamide | Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) | ↓ | ↑ | - |
| Na-K-2Cl sympoter blockers | Loss | Loop diuretics: Furosemide Bumetanide Torsemide | Ascending loop of Henle | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Na-Cl sympoter blockers | Through | Thiazides: Hydrochlorothiazide Chlorthalidone | Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Na channel blockers | Kidney | K-sparing diuretics: Amiloride Triamterene | Collecting tubule (CT) | ↑ | ↑ | - |
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA) | Kidney | K-sparing diuretics: Spironolactone Eplerenone | Collecting tubule (CT) | ↑ | ↑ | - |
Indications for Acute Dialysis {AEIOU}
- Acidosis
- Electrolyte disturbances
- Intoxication
- Overload of volume
- Uremia
Mechanisms of Dialysis
| Mechanism | Dialysis | Ultrafiltration |
|---|---|---|
| Transport | Diffusion | Convection |
| Drive | Concentration gradient | Pressure gradient |
| Removal | Small molecules | All molecules & Water |
| Fluids | Dialysate | Replacement fluid |
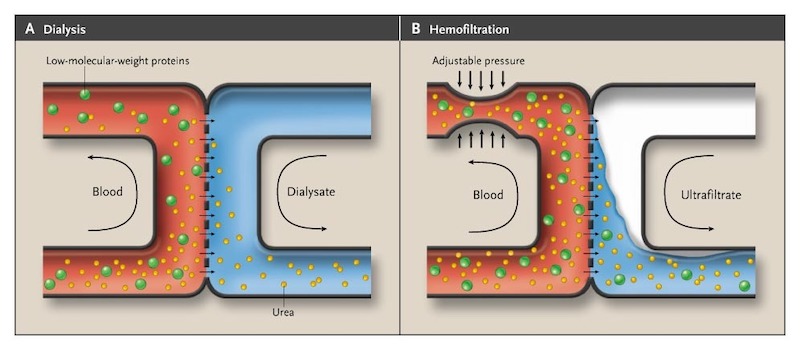
Modes of Dialysis
- Peritoneal dialysis (PD)
- Intermittent hemodialysis (IHD)
- Sustained low efficiency dialysis (SLED)
- Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT)
Presentation of Uremia
- Altered mental status (AMS)
- Asterixis
- Restlessness
- Serositis
- Nausea/Vomiting
- Uremic frost
- Bleeding
Classification of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
| Variable | Prerenal | Renal | Postrenal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urine osmolality | > 500 | < 350 | - |
| Urine Na | < 20 | > 40 | - |
| FENa | < 1% | > 2% | - |
| Serum BUN/Cr | > 20 | < 15 | - |
Staging of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
RIFLE
| Stage | Cr | GFR | Urine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk | 1.5x ~ 2x | 50 ~ 75% | < 0.5 mL/kg/h for 6 ~ 12 hours |
| Injury | 2x ~ 3x | 25 ~ 50% | < 0.5 mL/kg/h for 12 ~ 24 hours |
| Failure | > 3x ↑ > 0.5 mg/dL to > 4.0 mg/dL | < 25% | < 0.3 mL/kg/h for > 24 hours 0 mL/kg/h for > 12 hours |
| Loss | Failure > 4 weeks | ||
| ESRD | Failure > 3 months |
AKIN
| Stage | Cr | Urine |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5x ~ 2x ↑ > 0.3 mg/dL | < 0.5 mL/kg/h for 6 ~ 12 hours |
| 2 | 2x ~ 3x | < 0.5 mL/kg/h for 12 ~ 24 hours |
| 3 | > 3x ↑ > 0.5 mg/dL to > 4.0 mg/dL | < 0.3 mL/kg/h for > 24 hours 0 mL/kg/h for > 12 hours |
Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
| Stage | GFR |
|---|---|
| 1 | > 90 |
| 2 | 60 ~ 90 |
| 3a | 45 ~ 60 |
| 3b | 30 ~ 45 |
| 4 | 15 ~ 30 |
| 5 | < 15 |
Presentation of Glomerulopathy
Nephritis
- Proteinuria < 3.5 g/d
- Oliguria
- Azotemia
- Hypertension
- Hematuria
Nephrosis
- Proteinuria > 3.5 g/d
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Hypogammaglobulinemia
- Hypercoagulability
- Hyperlipidemia
Classification of Glomerulopathy {IAA-RAMD-MMF-DA}
| Glomerulopathy | Nephritis | Nephrosis | LM/IF/EM | IC Shape | IC Location | C3 | Associations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgA nephropathy [Berger disease] | + | - | Mesangial proliferation | Mesangial | Mesangial | - | HSP |
| Alport syndrome | + | - | GBM thinning GBM splitting Basket-weave appearance | - | - | - | - |
| Anti-GBM disease [Goodpasture syndrome] | + | - | Crescent shape | Linear | GBM | - | - |
| ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) | + | - | Crescent shape | - | - | - | - |
| Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) | + | - | Crescent shape | - | - | - | Anti-GBM ANCA |
| Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis (APGN) | + | - | Lumpy-bumpy appearance Starry sky appearance | Granular | Subepithelial | ↓ | GAS |
| Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) | + | + | Mesangial proliferation GBM thickening GBM splitting Tram-track appearance | Granular | Subendothelial | ↓ | SLE HBV HCV |
| Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis (DPGN) | + | + | Wire looping appearance | Granular | Subendothelial | ↓ | SLE |
| Membranous nephropathy | - | + | GBM thickening Spike-and-dome appearance | Granular | Subepithelial | - | Anti-PLA2R SLE HBV HCV |
| Minimal change disease (MCD) | - | + | Podocyte effacement | - | - | - | - |
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) | - | + | Segmental sclerosis Hyalinosis Podocyte effacement | - | - | - | HIV SCD |
| Diabetic nephropathy | - | + | Nodular sclerosis GBM thickening | - | - | - | - |
| Amyloid nephropathy | - | + | Nodular sclerosis | - | - | - | - |
Etiology of Acute Interstitial Nephritis (AIN)
- Drugs
- Analgesics :: NSAIDs
- Antibiotics
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPI)
- Infections
- Tuberculosis
- Legionella
- CMV
- Autoimmune
- SLE
- Sjogren syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
Etiology of Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
- Ischemia
- Drug-induced nephrotoxicity
- Analgesics :: NSAIDs
- Antibiotics :: Vancomycin & Aminoglycosides & Amphotericin B
- Antivirals :: DNA polymerase inhibitors
- Antineoplastics :: Platinums [-Platins]
- Contrast-induced nephropathy
- Hematuria :: hemoglobinuria & myoglobinuria
- Light chain deposition disease (LCDD)
Etiology of Renal Papillary Necrosis (RPN) {SAND}
- Sickle cell nephropathy
- Acute pyelonephritis
- NSAIDs
- Diabetic nephropathy
Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA)
| Type | Synonym | Defect | Serum K | Serum H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Distal | H secretion | ↓ | ↑ |
| 2 | Proximal | HCO3 reabsorption | ↓ | ↑ |
| 3 | Mixed | - | ↓ | ↑ |
| 4 | Hyperkalemic | Aldosterone | ↑ | ↑ |
Etiology of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Bladder stone
- Urinary retention
- Neurogenic bladder
- Drug-induced
Etiology of Underactive Bladder (UAB)
- Overdistension
- Postoperative
- Neurogenic bladder
- Drug-induced
Urinary Incontinence
| Type | Urgency | Nocturia | Residual volume | Etiology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stress | - | - | - | Pelvic relaxation |
| Urge | + | + | ↓ | Overactive bladder (OAB) |
| Overflow | - | + | ↑ | Underactive bladder (UAB) |
Etiology of Stress Incontinence
- Urethral hypermobility
- Intrinsic sphincteric deficiency
- Pelvic organ prolapse (POP)
Etiology of Urinary Retention
- Obstruction
- Underactive bladder (UAB)
International Classification of Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR)
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Reflux to the ureter |
| 2 | Reflux to the pelvis |
| 3 | Dilatation of the ureter & pelvis & calyx |
| 4 | Blunting of the fornix |
| 5 | Loss of papillary impressions |
.jpg)
Indications for Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG)
- Boys with first UTI
- Girls < 3 y/o with first UTI
- Girls < 5 y/o with febrile UTI
- Girls with recurrent UTIs
Pathogens of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
- Serratia marcescens
- Escherichia coli
- Enterobacter cloacae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Proteus mirabilis
- Candida
Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Voided urine > 105 CFU/mL
- Catheterized urine > 5 × 104 CFU/mL
- Suprapubic aspirate > 104 CFU/mL
Empirical Antibiotics for Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
| Patient | Antibiotics |
|---|---|
| Outpatient | Nitrofurantoin TMP-SMX Fosfomycin Amoxicillin & Clavulanate 1° Cephalosporins |
| Outpatient & Complicated | 3° Cephalosporins Fluoroquinolones |
| Inpatient | 3° Cephalosporins Fluoroquinolones |
| Inpatient & Complicated | Vancomycin & Carbapenems |
Complicated Outpatients
- Temperature > 38°C
- Costovertebral angle tenderness
- Pain :: pelvic / perineal
Management After Bladder Scan
| Timing | Volume (mL) | Managment |
|---|---|---|
| PVR | < 200 | - |
| PVR | 200 ~ 400 | Intermittent catheterization |
| PVR | > 400 | Indwelling urinary catheter |
| Random | < 400 | Bladder scan Q2H |
| Random | > 400 | Indwelling urinary catheter |
- Post-voidal residual (PVR)