Endocrine System
Growth Hormone Disorders
| Disorder | GHRH | GH | IGF-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laron syndrome | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Hypopituitarism | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ |
| Acromegaly | ↑ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
Growth Hormone Stimulation Tests
- Insulin
- Glucagon
- Arginine
- Clonidine
- Propranolol
Medications for Acromegaly
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| Somatostatin agonists | Octreotide Lanreotide |
| GH antagonists | Pegvisomant |
| D2 agonists | Bromocriptine Cabergoline |
Treatment of Hyperprolactinemia
| Mechanism | Medication | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| D2 agonists | Bromocriptine | Hyperprolactinemia |
| Cabergoline | Hyperprolactinemia |
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
| Step | Enzyme |
|---|---|
| Oxidation | Thyroperoxidase (TPO) |
| Organification | Thyroperoxidase (TPO) |
| Coupling | Thyroperoxidase (TPO) |
| Deiodination | 5'-deiodinase |
Thyroid Hormone Disorders
| Disorder | TRH | TSH | TH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subclinical hypothyroidism | ↑ | ↑ | - |
| 1° Hypothyroidism | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| 2° Hypothyroidism | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ |
| Subclinical hyperthyroidism | ↓ | ↓ | - |
| Struma ovarii | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| 1° Hyperthyroidism | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| 2° Hyperthyroidism | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
Presentation of Hypothyroidism {WAS-TIRED}
- Weight gain
- Ataxia
- Short stature
- Tired
- Intolerance to cold
- Reflex delayed
- Edema :: myxedema
- Dry skin
Presentation of Congenital Hypothyroidism
- Developmental delay
- Failure to thrive
- Large anterior fontanelle
- Coarse facies
- Macroglossia
- Umbilical hernia
Presentation of Hyperthyroidism {SWEATING}
- Sweating
- Weight loss
- Emotional lability
- Edema :: pretibial myxedema
- ↑ Appetite
- Tremor
- Tachycardia
- Intolerance to heat
- Nervousness
- Goiter
Workup of 1° Hyperthyroidism
| Cause | RAI | Thyroglobulin |
|---|---|---|
| Graves disease | ↑ | ↑ |
| Multinodular goiter | ↑ | - |
| Toxic adenoma | ↑ | - |
| Thyroiditis | ↓ | ↑ |
| Exogenous TH | ↓ | ↓ |
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
- Thyroid peroxidase inhibitors
- Propylthiouracil
- Methimazole
- Iodine [Lugol] solution
- Deiodinase inhibitors
- Propylthiouracil
- Propranolol
- Corticosteroids
- β antagonists :: Propranolol
- Radioiodine ablation
- Surgery
Parathyroidism Hormone Disorders
| Disorder | PTH | Ca | P | Bone Disorder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1° Hypoparathyroidism | ↓ (1°) | ↓ | ↑ | - |
| PTH-independent hypercalcemia | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑/↓ (1°) | - |
| 1° Hyperparathyroidism | ↑ (1°) | ↑ | ↓ | Osteitis fibrosa cystica |
| 2° Hyperparathyroidism | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↑ (1°) | Renal osteodystrophy |
| 3° Hyperparathyroidism | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | Renal osteodystrophy |
| Vitamin D deficiency | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ (1°) | Rickets Osteomalacia |
| Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP) | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↑ (1°) | Albright hereditary osteodystrophy |
| Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | - |
Presentation of Hyperparathyroidism
- Stones
- Renal stones
- Bones
- Brown tumor
- Osteitis fibrosa cystica
- Groans
- Constipation
- Psychiatric overtones
- Depression
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
| Deficiency | Mineralocorticoid | Glucocorticoid | Androgen | BP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21-Hydroxylase | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ |
| 11-Hydroxylase | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 17-Hydroxylase | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
Mineralocorticoid Disorders
| Disorder | Renin | Mineralocorticoid | Na & BP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ |
| CAH :: 21-Hydroxylase deficiency | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ |
| CAH :: 11-Hydroxylase deficiency | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
| CAH :: 17-Hydroxylase deficiency | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
| Conn syndrome | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
| Adrenal tumor | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
| Exogenous steroid | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
| Renin-secreting tumor | ↑ (1°) | ↑ | ↑ |
| Hypotension | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
Glucocorticoid Disorders
| Disorder | CRH | ACTH | Glucocorticoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Addison disease | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Hypopituitarism | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ |
| Exogenous steroid | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| Adrenal tumor | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| Ectopic ACTH | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
| Cushing disease | ↓ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ |
Diagnosis of Cushing Syndrome
- 24-hour urine cortisol
- Dexamethasone suppression test :: low-dose
- Midnight salivary cortisol
- Midnight serum cortisol
Sex Hormone Disorders
| Disorder | GnRH | LH & FSH | SH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Klinefelter syndrome | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Turner syndrome | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Menopause [Ovarian failure] | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Resistant ovary [Savage] syndrome | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ (1°) |
| Hypopituitarism | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ |
| Kallmann syndrome | ↓ (1°) | ↓ | ↓ |
| Hypothyroidism | ↓ (1°) | ↓ | ↓ |
| Hyperprolactinemia | ↓ (1°) | ↓ | ↓ |
| Pregnancy | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| Germ cell tumor | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| Exogenous steroid | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ (1°) |
| Androgen insensitive syndrome (AIS) | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | ↓/↑ |
ADH Disorders
| Diagnosis | ADH | Osmolarity |
|---|---|---|
| Polydipsia | ↓ | ↓ (1°) |
| Central DI | ↓ (1°) | ↑ |
| Nephrogenic DI | ↑ | ↑ (1°) |
| SIADH | ↑ (1°) | ↓ |
Etiology of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
- Mutations
- Vasopressin receptor
- Aquaporin
- Electrolyte disturbances
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hematologic disorders
- Sickle cell disease
- Multiple myeloma
- Autoimmune diseases
- Sjogren syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Amyloidosis
- Drugs
- Lithium
- Demeclocycline
Medications for Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
- NSAIDs :: Indomethacin
- Thiazides :: Hydrochlorothiazide
Etiology of Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of ADH (SIADH)
- Malignancies :: small cell carcinoma
- CNS disorders
- Pulmonary diseases
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumonia
- Drugs
- Carbamazepine
- Cyclophosphamide
- SSRIs
Treatment of Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of ADH (SIADH)
- Fluid restriction
- V2 antagonists :: -Vaptans
- Nephrogenic DI-inducing drugs
- Lithium
- Demeclocycline
Insulin Disorders
| Disorder | Insulin | Glucose |
|---|---|---|
| Starvation | ↓ | ↓ (1°) |
| DM type 1 | ↓ (1°) | ↑ |
| DM type 2 | ↑ | ↑ (1°) |
| Insulinoma | ↑ (1°) | ↓ |
Presentation of Glucagonoma {4D}
- Depression
- Dermatitis :: necrolytic migratory erythema
- Diabetes
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Whipple Triad of Insulinoma
- Symptoms of hypoglycemia
- Fasting hypoglycemia :: < 50 mg/dL
- Relief of symptoms on IV glucose
Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus
| Diagnosis | FBG | OGTT | HbA1c |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | < 100 mg/dL | 50-g 1-hour < 140 mg/dL | < 6.5% |
| Gestational | < 125 mg/dL | 50-g 1-hour > 140 mg/dL 100-g 3-hour ≥ 2/4 | - |
| Overt | > 125 mg/dL | 75-g 2-hour > 200 mg/dL | > 6.5% |
Medications for Diabetes Mellitus
| Mechanism | Effects | Medication | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
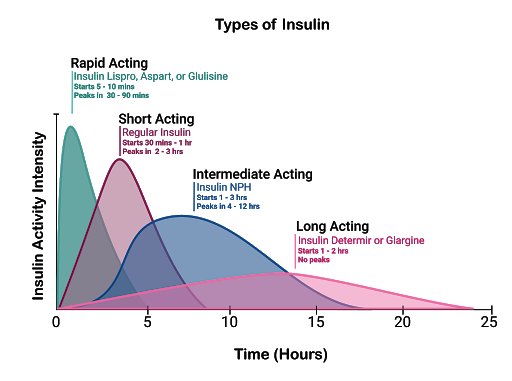
| Insulin | ↑ Insulin | Rapid acting: Lispro Aspart Glulisine | DM |
| Short acting: Regular insulin | DM | ||
| Intermediate acting: NPH insulin | DM | ||
| Long acting: Glargine Detemir | DM | ||
| K channel blockers | ↑ Insulin | 1° Sulfonylureas: Tolbutamide Chlorpropamide | DM type 2 |
| 2° Sulfonylureas: Glimepiride Glipizide Glyburide | DM type 2 | ||
| Meglitinides [-Glinides] | DM type 2 | ||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | ↑ Insulin ↓ Glucagon | -Gliptins | DM type 2 |
| GLP-1 analogs | ↑ Insulin ↓ Glucagon | Exenatide Liraglutide Semaglutide | DM type 2 |
| Amylin analogs | ↓ Glucagon | Pramlintide | DM |
| α-Glucosidase inhibitors | ↓ Glucose | Acarbose Miglitol | DM type 2 |
| SGLT-2 inhibitors | ↓ Glucose | -Gliflozins | DM type 2 |
| AMPK inducers | ↑ Insulin sensitivity | Biguanides: Metformin | DM type 2 |
| PPAR-γ inducers | ↑ Insulin sensitivity | Thiazolidinediones [-Glitazones] | DM type 2 |
Treatment of Acute Hyperglycemia
- Fluids :: isotonic saline
- Potassium
- Insulin
- Bicarbonate if indicated
- Phosphate if indicated
Microvascular Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
- Retinopathy
- Nephropathy
- Neuropathy
Insensitivity of Endocrine Receptors
| Receptor | Disease |
|---|---|
| GH | Laron syndrome |
| PTH | Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP) |
| LH & FSH | Resistant ovary [Savage] syndrome |
| Androgen | Androgen insensitive syndrome (AIS) |
| Insulin | Diabetes mellitus type 2 |
| Vasopressin | Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (DI) |
Endocrine Tests
| Test | Indication | Positive | Negative |
|---|---|---|---|
| GH stimulation test | ↓ Pituitary | Hypopituitarism | - |
| GnRH stimulation test | ↓ Pituitary | Hypopituitarism | - |
| Precocious puberty | Peripheral precocious puberty | Central precocious puberty | |
| Progestin challenge test | 2° Amenorrhea | Non-anovulation | Anovulation |
| TRH stimulation test | ↓ Pituitary | Hypopituitarism | - |
| ACTH stimulation test | ↓ Cortisol | 1° Adrenal insufficiency | 2° Adrenal insufficiency |
| Dexamethasone suppression test :: low-dose | ↑ Cortisol | Cushing syndrome | - |
| Dexamethasone suppression test :: high-dose | ACTH-dependent Cushing syndrome | Ectopic ACTH | Cushing disease |
| Saline suppression test | ↑ Aldosterone | 1° Hyperaldosteronism | - |
| Oral glucose tolerance test | ↑ Glucose | Diabetes mellitus | - |
| Water deprivation test | Polyuria | Diabetes insipidus | Polydipsia |
| Desmopressin challenge test | Diabetes insipidus | Nephrogenic DI | Central DI |
Neuroendocrine Tumors (NET)
Ectodermal Origin
| Origin | Tumors |
|---|---|
| Surface ectoderm | Craniopharyngioma Pituitary adenoma |
| Neuroectoderm :: neural tube | Pinealoma |
| Neuroectoderm :: neural crest | Pheochromocytoma Paraganglioma |
Endodermal Orign
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Parathyroid tumors
- Carcinoid tumors
- Gastrinoma
- VIPoma
- Insulinoma
- Glucagonoma
- Small cell carcinoma
- Large cell carcinoma
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasias (MEN)
MEN Type 1
- Pituitary adenoma
- Parathyroid tumors
- Pancreatic endocrine tumors
MEN Type 2A
- Parathyroid tumors
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Pheochromocytoma
MEN Type 2B
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Pheochromocytoma
- Mucosal neuroma