Metabolism
Free Water Deficit (FWD)
| Parameter | 0.6 × W × (Na ÷ 140 - 1) |
|---|---|
| W | Weight (kg) |
| Na | Serum sodium (mEq/L) |
Crystalloids
| Solution | Na (mEq/L) | K (mEq/L) | Ca (mg/dL) | Cl (mEq/L) | Glucose (g/dL) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% dextrose in water (D5W) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 3.5 ~ 6.5 |
| 5% dextrose in normal saline (D5NS) | 154 | 0 | 0 | 154 | 5 | 3.5 ~ 6.5 |
| Normal saline (NS) | 154 | 0 | 0 | 154 | 0 | 4.5 ~ 7 |
| Ringer's lactate | 130 | 4 | 1.35 | 109 | 0 | 6 ~ 7.5 |
| Ringer's acetate | 130 | 5 | 1 | 112 | 0 | 6 ~ 8 |
Rate of Fluid Administration
| Weight (kg) | Rate (mL/kg/h) | Rate (mL/kg/d) |
|---|---|---|
| < 10 | 4 | 100 |
| 10 ~ 20 | 2 | 50 |
| > 20 | 1 | 20 |
Parkland Formula of Fluid Requirement for Burns
| Parameter | W × TBSA × 4 |
|---|---|
| W | Weight (kg) |
| TBSA | Total body surface area (%) |
- 1/2 in the 1st 8 hours
- 1/2 in the next 16 hours
Acid-Base Disturbances
| Disturbance | pH | HCO3 | PaCO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic acidosis | ↓ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ 1.25 ΔHCO3 |
| Metabolic alkalosis | ↑ | ↑ (1°) | ↑ 0.75 ΔHCO3 |
| Respiratory acidosis | ↓ | ↑ 0.1 ~ 0.4 ΔPaCO2 | ↑ (1°) |
| Respiratory alkalosis | ↑ | ↓ 0.2 ~ 0.4 ΔPaCO2 | ↓ (1°) |
Workup of Metabolic Acidosis
- Anion gap :: normal
- Urine anion gap :: negative
- Saline
- Diarrhea
- VIPoma
- Urine anion gap :: positive {HARD}
- Hypoaldosteronism
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
- Renal failure
- Diuretics :: Acetazolamide & K-sparing diuretics
- Urine anion gap :: negative
- Anion gap :: high {MUDPILES}
- Methanol
- Uremia
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Propylene glycol
- Iron & Isoniazid
- Lactate
- Ethanol & Ethylene glycol
- Salicylates
Workup of Metabolic Alkalosis
- Urine Cl < 20 [Saline-responsive]
- Vomiting
- Cystic fibrosis
- Urine Cl > 20 [Saline-resistant]
- Normotensive
- Diuretics :: Loop diuretics & Thiazides
- Bartter syndrome
- Gitelman syndrome
- Hypertensive
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Liddle syndrome
- Syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess (SAME)
- Normotensive
ECG Changes in Electrolyte Disturbances
Hypokalemia
- Flattened T waves
- U waves
Hyperkalemia
- Flattened P waves
- Widened QRS complexes
- Peaked T waves
- Sine waves
Hypocalcemia
- Prolonged QT interval
- Bradycardia
Hypercalcemia
- Shortened QT interval
- Tachycardia
Sodium Correction for Hyperglycemia
| Parameter | Na + 0.024 × (Glucose - 100) |
|---|---|
| Na | Serum sodium (mEq/L) |
| Glucose | Serum glucose (mg/dL) |
Workup of Hyponatremia
- Serum osmolality < 280 mOsm/kg [Hypotonic]
- Volume status :: hypovolemic
- Urine Na < 20 & FENa < 1%
- GI losses
- Skin losses
- Third spacing
- Urine Na > 20 & FENa > 1%
- Diuretics
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Urine Na < 20 & FENa < 1%
- Volume status :: euvolemic
- Urine osmolality < 100 mOsm/kg
- Polydipsia
- Urine osmolality > 100 mOsm/kg
- SIADH
- Hypothyroidism
- Urine osmolality < 100 mOsm/kg
- Volume status :: hypervolemic
- Urine Na < 20 & FENa < 1%
- Heart failure
- Hepatic failure
- Urine Na > 20 & FENa > 1%
- Renal failure
- Urine Na < 20 & FENa < 1%
- Volume status :: hypovolemic
- Serum osmolality 280 ~ 295 mOsm/kg [Isotonic]
- Hyperlipidemia
- Hyperproteinemia
- Serum osmolality > 295 mOsm/kg [Hypertonic]
- Hyperglycemia
Management of Hyponatremia
| Volume Status | Management |
|---|---|
| Hypovolemic | Normal saline |
| Euvolemic | Fluid restriction |
| Hypervolemic | Fluid restriction ± Diuretics |
Workup of Hypernatremia
- Urine osmolality < 600 mOsm/kg
- Diabetes insipidus
- Diuretics :: osmotic
- Urine osmolality > 600 mOsm/kg
- Urine Na < 25
- GI losses
- Skin losses
- Seizures
- Eexercise
- Urine Na > 100
- Fluids :: hypertonic saline
- Urine Na < 25
Etiology of Hypokalemia
- Extra-renal losses
- Vomiting
- Cystic fibrosis
- Diarrhea
- VIPoma
- Renal losses
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) :: type 1 & 2
- Diuretics :: Acetazolamide & Loop diuretics & Thiazides
- Bartter syndrome
- Gitelman syndrome
- Liddle syndrome
- Syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess (SAME)
Etiology of Hyperkalemia
- Pseudohypokalemia
- Insulin deficiency
- β antagonists
- Hypoaldosteronism
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) :: type 4
- Renal failure
- Diuretics :: K-sparing diuretics
- High anion gap metabolic acidosis
Treatment of Hyperkalemia
- Insulin & Glucose
- β agonists :: Albuterol
- Bicarbonate
- Calcium
- Polystyrene sulfonate: Kalimate & Kayexalate
- Diuretics :: Loop diuretics
Calcium Correction for Hypoalbuminemia
| Parameter | 0.8 × (4 - Albumin) + Ca |
|---|---|
| Ca | Serum calcium (mg/dL) |
| Albumin | Serum albumin (g/dL) |
Presentation of Hypocalcemia
- Bradycardia
- Paresthesia
- Prolonged QT interval
- Tetany
- Chvostek sign
- Trousseau sign
Etiology of Hypocalcemia
- Chronic kidney disease
- 1° Hypoparathyroidism
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP)
Presentation of Hypercalcemia
- Tachycardia
- Shortened QT interval
- Weakness
- Constipation
- Polyuria
- Kidney stones
- Bone pain
- Psychiatric overtones
Etiology of Hypercalcemia {CHIMPANZEES}
- Calcium supplementation
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperthyroidism
- Iatrogenic
- Immobility
- Milk-alkali syndrome
- Paget disease
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Acromegaly
- Neoplasm
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Excess vitamin A
- Excess vitamin D
- Sarcoidosis
Treatment of Hypercalcemia
- Hydration
- Diuretics :: Loop diuretics
- Calcitonin
- Bisphosphonates
- Corticosteroids
- Dialysis
Iron Disorders
| Disorder | Fe | Ferritin | Transferrin [TIBC] | Saturation = Fe ÷ TIBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thalassemia | - | - | - | - |
| Anemia of chronic disorders | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | - |
| Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ |
| Lead poisoning | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Sideroblastic anemia | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Hemochromatosis | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Pregnancy & OCP | - | - | ↑ | ↓ |
Presentation of Iron Deficiency
- Iron deficiency anemia (IDA)
- Koilonychia
- Pica
- Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- Dysphagia
- Esophageal web
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Restless legs syndrome (RLS)
Presentation of Hemochromatosis
- Skin pigmentation
- Cardiomyopathy
- Hepatomegaly
- Cirrhosis
- Diabetes melitus
- Hypogonadism
- Arthropathy
- Pseudogout
Treatment of Hemochromatosis
- Phlebotomy
- Chelation
- Deferasirox
- Deferoxamine
- Deferiprone
Presentation of Copper Deficiency
- ↓ Wound healing
- Easy bruising
- Brittle hair
- Ataxia
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Sideroblastic anemia
Presentation of Wilson Disease
- Kayser-Fleischer rings
- Cirrhosis
- Fanconi syndrome
- Parkinsonism
Treatment of Wilson Disease
- Zinc
- Chelation
- Penicillamine
- Trientine
Presentation of Zinc Deficiency
- ↓ Wound healing
- Easy bruising
- Alopecia
- Dermatitis
- Diarrhea
- Male hypogonadism
- Dysgeusia
- Anosmia
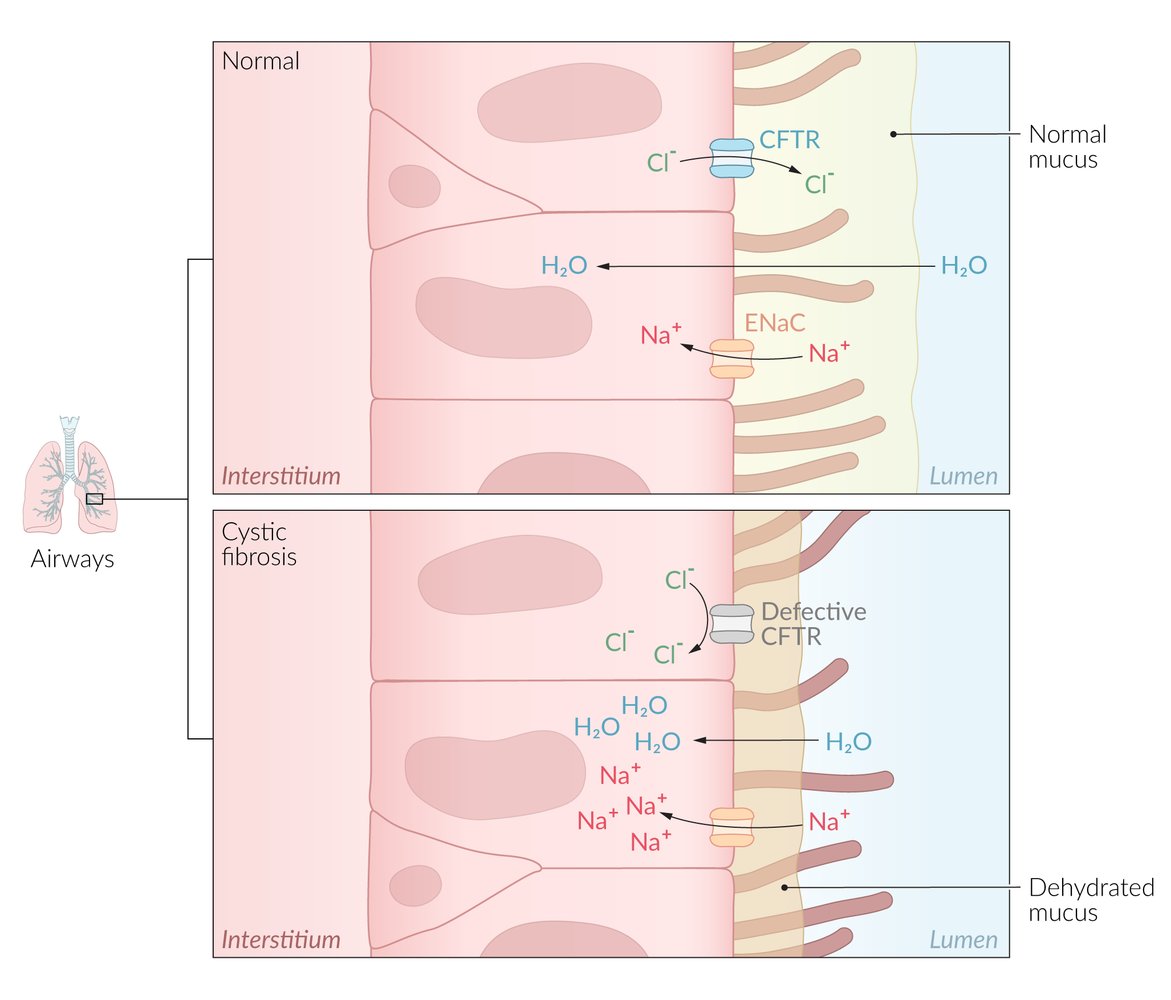
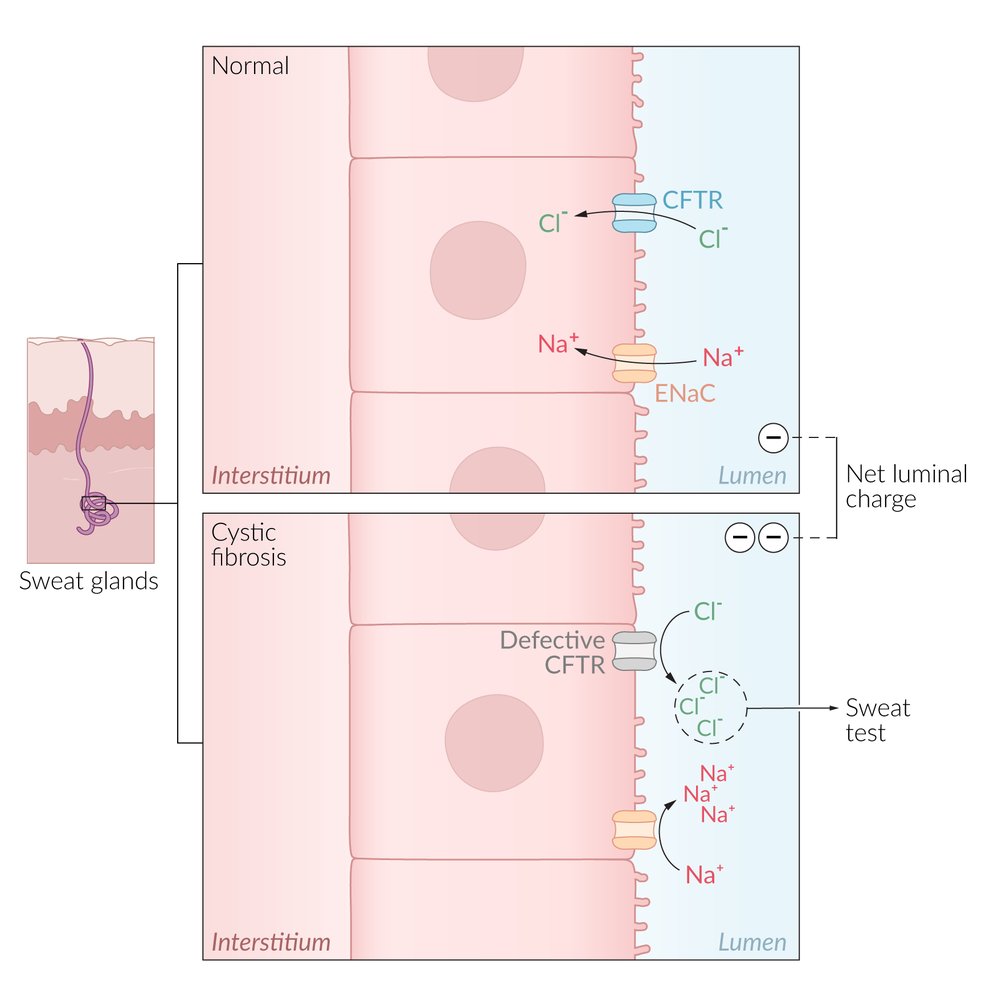
Electrolyte Changes in Cystic Fibrosis
- ↓ NaCl in lungs
- ↓ NaCl in pancreatic ducts
- ↑ NaCl in sweat glands
Presentation of Vitamin Deficiency
| Vitamin | Deficiency |
|---|---|
| A | Night blindness Xeroderma Xerophthalmia Bitot spots |
| B1 | Dry beriberi Wet beriberi Wernicke encephalopathy Korsakoff syndrome Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome |
| B2 {2C} | Cheilosis Corneal vascularization |
| B3 {3D} | Dermatitis :: pellagra Diarrhea Dementia |
| B6 | Homocystinuria Sideroblastic anemia Peripheral neuropathy |
| B7 | Dermatitis Alopecia |
| B9 | Homocystinuria Megaloblastic anemia Neural tube defect |
| B12 | Homocystinuria Megaloblastic anemia Methylmalonic acidemia Subacute combined degeneration |
| C | Scurvy ↓ Wound healing Easy bruising |
| D | Rickets Osteomalacia Hypocalcemia Hypophosphatemia |
| E | Hemolytic anemia |
| K | Coagulopathy Easy bruising |
Classic Triad of Wernicke Encephalopathy {CAO}
- Confusion
- Ataxia
- Ophthalmoplegia
Etiology of Vitamin B3 [Niacin] Deficiency
- Carcinoid syndrome
- Hartnup disease
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) deficiency
Etiology of Vitamin B9 [Folate] Deficiency
- Alcoholism
- Crohn disease
- Malabsorption syndromes
- Drugs
- Methotrexate
- Phenytoin
- Sulfonamides
- Trimethoprim
Etiology of Vitamin B12 [Cobalamin] Deficiency
- Achlorhydria
- Crohn disease
- Diphyllobothrium latum
- Gastrectomy
- Gastritis
- Ileal resection
- Malabsorption syndromes
- Metformin
- Pernicious anemia
Etiology of Vitamin K Deficiency
- Biliary atresia
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics
- Crohn disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
- Newborns
- Steatorrhea
- Vitamin E intoxication
Harris-Benedict Adjustment of Energy Expenditure
| Condition | Calorie (BEE) | Protein (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary | 1.2 | 0.8 ~ 1 |
| Postoperation | 1.3 ~ 1.5 | 1.2 ~ 1.6 |
| Burns | 1.6 ~ 2.0 | 1.5 ~ 2 |
Curreri Formula of Energy Expenditure for Burns
| Parameter | 25 × W + 40 × TBSA |
|---|---|
| W | Weight (kg) |
| TBSA | Total body surface area (%) |
Glycogen Storage Diseases (GSD)
| Disease | Defects | Hypoglycemia | Hepatomegaly | Myopathy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Von Gierke disease | Glucose-6-phosphatase | + | + | - |
| Pompe disease | α-1,4-Glucosidase :: lysosomal | - | + | + |
| Cori disease | Debranching enzyme | + | + | + |
| Anderson disease | Branching enzyme | - | + | - |
| McArdle disease | Glycogen phosphorylase :: musclular | - | - | + |
| Hers disease | Glycogen phosphorylase :: hepatic | + | + | - |
Lysosomal Storage Diseases (LSD)
Glycogenosis
| Disease | Defects | Findings | Hepatomegaly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pompe disease | α-1,4-Glucosidase | - | + |
Sphingolipidosis
| Disease | Defects | Findings | Hepatomegaly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gaucher disease | Glucocerebrosidase | Gaucher cell | + |
| Niemann-Pick disease | Sphingomyelinase | Cherry-red spot | + |
| Tay-Sachs disease | Hexosaminidase | Cherry-red spot | - |
| Fabry disease | α-Galactosidase | Peripheral neuropathy | - |
| Krabbe disease | Galactocerebrosidase | Leukodystrophy | - |
| Metachromatic leukodystrophy | Arylsulfatase | Leukodystrophy | - |
Mucolipidosis
| Disease | Defects | Findings | Hepatomegaly |
|---|---|---|---|
| I-cell disease | Phosphotransferase | Corneal clouding | + |
Mucopolysaccharidosis
| Disease | Defects | Findings | Hepatomegaly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hurler syndrome | α-Iduronidase | Corneal clouding | + |
| Hunter syndrome | Iduronate sulfatase | - | - |
Metabolic Disorders
| Disorder | Defects | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Alkaptonuria (AKU) | Homogentisate oxidase | ↑ Homogentisic acid |
| Cystinuria | Amino acid transporter | ↓ COLA |
| Hartnup disease | Amino acid transporter | ↓ Tryptophan |
| Homocystinuria | Cystathionine synthase | ↑ Homocysteine ↓ Cysteine |
| Methionine synthase | ↑ Homocysteine ↓ Methionine | |
| Lesch-Nyhan syndrome | HGPRT | ↑ Uric acid |
| Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) | Branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase | ↑ α-ketoacids |
| Methylmalonic acidemia | Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase | ↑ Methylmalonic acid |
| Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency | Ornithine transcarbamylase | ↑ Orotic acid ↑ Ammonia ↓ Urea |
| Orotic aciduria | UMP synthase | ↑ Orotic acid ↓ DNA |
| Phenylketonuria (PKU) | Phenylalanine hydroxylase Tetrahydrobiopterin | ↑ Phenylalanine ↓ Tyrosine |
Symptoms of Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome {HGPRT}
- Hyperuricemia
- Gout
- Psychosis :: aggression & self-mutilation
- Retardation :: intellectual disability
- Dystonia
Metabolic Syndrome
- Abdominal obesity
- Hypertension: BP ≥ 130/85 mmHg
- Hyperglycemia: FBG ≥ 100 mg/dL
- Hypertriglycemia: triglyceride ≥ 150 mg/dL
- Low HDL cholesterol
- HDL < 40 mg/dL in men
- HDL < 50 mg/dL in women
Presentation of Hyperlipidemia
- Xanthomas
- Xanthelasma
- Corneal arcus
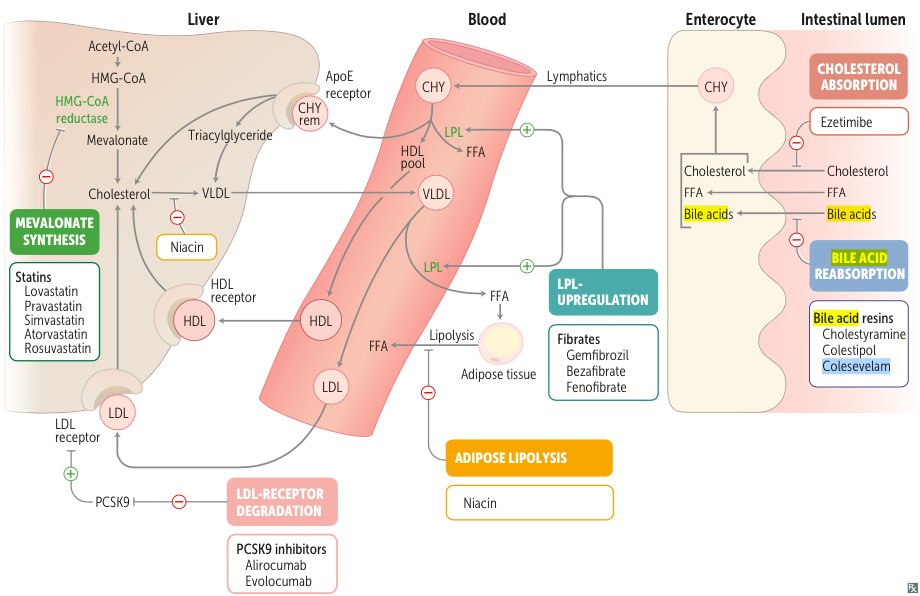
Medications for Hyperlipidemia {OECSNF}
| Mechanism | Medication | LDL | HDL | Triglyceride |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreatic lipase inhibitors | Orlistat | ↓↓ | - | - |
| Cholesterol absorption inhibitors | Ezetimibe | ↓↓ | - | - |
| Bile acid resin | Cholestyramine Colestipol Colesevelam | ↓↓ | - | - |
| HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors | Statins | ↓↓↓ | ↑ | ↓ |
| HSL & VLDL synthesis inhibitors | Niacin (B3) | ↓↓ | ↑↑ | ↓ |
| LPL & PPAR-α inducers | Fibrates | ↓ | ↑ | ↓↓↓ |
Indications for Statin Therapy
- History of arterial thromboembolism
- LDL > 190 mg/dL
- Age > 40 years & Diabetes mellitus
- 10-year ASCVD risk > 7.5% ~ 10%
Treatment of Morbid Obesity
- GLP-1 analogs
- Orlistat
- Phentermine-Topiramate
- Bariatric surgery
Collagen Releated Diseases
| Component | Diseases |
|---|---|
| Type 1 collagen | Osteogenesis imperfecta |
| Type 2 collagen | - |
| Type 3 collagen | Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) |
| Type 4 collagen | Alport syndrome Goodpasture syndrome |
| Type 5 collagen | Classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) |
| Elastin | α1-antitrypsin deficiency |
| Fibrillin | Marfan syndrome |
Etiology of Marfanoid Habitus
- Marfan syndrome
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) 2B
- Homocystinuria
Indications for Low-Protein Diet
- Liver failure → Hyperammonemia
- End stage renal disease (ESRD) → Uremia
Amyloidosis
| Disease | Amyloid | Precursor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary amyloidosis | Amyloid light-chain (AL) | Immunoglobulin light-chain |
| Secondary amyloidosis | Amyloid A (AA) | Serum amyloid A (SAA) |
| Dialysis-related amyloidosis | Amyloid β2-microglobulin (Aβ2M) | β2-microglobulin (β2M) |
| DM type 2 | Amyloid islet amyloid polypeptide (AIAPP) | Islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) |
| Medullary thyroid cancer | Calcitonin | Calcitonin |
| Alzheimer disease | Amyloid β (Aβ) | Amyloid precursor protein (APP) |
| Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease | Amyloid prion protein (APrP) | Prion protein (PrP) |
| Familial amyloidosis | Amyloid transthyretin (ATTR) | Transthyretin (TTR) |