Nervous System
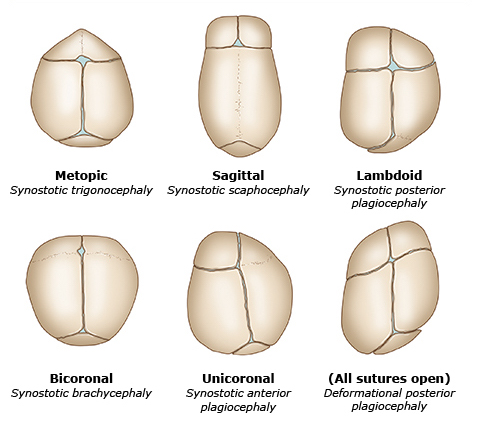
Craniosynostosis
| Type | Premature Suture |
|---|---|
| Trigonocephaly | Metopic |
| Scaphocephaly [Dolichocephaly] | Sagittal |
| Brachycephaly | Coronal |
| Plagiocephaly :: anterior | Unilateral coronal |
| Plagiocephaly :: posterior | Unilateral lambdoid |
Indications for CT Imaging for Head Trauma
PECARN Rule
- GCS < 15
- Altered mental status
- Suspected skull fracture
- Non-frontal scalp hematoma
- LOC > 5 seconds
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dangerous mechanism
Canadian CT Head Rule
- GCS < 15 at 2 hours after injury
- Suspected skull fracture
- Vomiting ≥ 2 episodes
- Age > 65 years
- Retrograde amnesia
- Dangerous mechanism
Signs of Basilar Skull Fracture
- Racoon eyes
- Battle sign
- CSF otorrhea
- CSF rhinorrhea
- Hemotympanum
Cortical Signs
| Lobe | Area | Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal | Prefrontal cortex | Personality changes |
| Frontal eye fields (FEF) | Ipsilateral conjugate deviation | |
| Broca area :: dominant | Broca aphasia | |
| Motor cortex | Contralateral paralysis | |
| Parietal | Sensory cortex | Contralateral paresthesia |
| Arcuate fasciculus :: dominant | Conduction aphasia | |
| Association cortex :: dominant | Gerstmann syndrome: Acalculia Agraphia Finger agnosia | |
| Association cortex :: nondominant | Contralateral hemineglect Constructional apraxia Dressing apraxia | |
| Superior optic radiation | Contralateral inferior quadrantanopia | |
| Temporal | Wernicke area :: dominant | Wernicke aphasia |
| Meyer loop | Contralateral superior quadrantanopia | |
| Occipital | Visual cortex | Contralateral hemianopia |
Hemorrhage
Extracranial
| Hemorrhage | Vessels | Bounded |
|---|---|---|
| Caput succedaneum | Soft tissues | - |
| Subgaleal | Subgaleal vessels | - |
| Cephalohematoma | Subperiosteal vessels | + |
Intracranial
| Hemorrhage | Vessels | Bounded |
|---|---|---|
| Epidural | Middle meningeal artery | + |
| Subdural | Bridging veins | - |
| Subarachnoid | Aneurysm Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) | - |
| Intraparenchymal | Microaneurysm Lipohyalinosis Amyloid angiopathy | - |
Risk of Progression of TIA to Ischemic Stroke {ABCD2}
- Age > 60 years
- BP > 140/90 mmHg
- Clinical features
- Unilateral weakness
- Speech impairment
- Duration
- Diabetes
Presentation of Ischemic Stroke
| Artery | Lesions | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Middle cerebral artery (MCA) | Motor cortex :: upper Sensory cortex :: upper Wernicke area Broca area Frontal eye fields (FEF) | Contralateral facial palsy Contralateral paralysis Contralateral paresthesia Aphasia Hemineglect |
| Anterior cerebral artery (ACA) | Motor cortex :: lower Sensory cortex :: lower | Contralateral paralysis Contralateral paresthesia |
| Posterior cerebral artery (PCA) | Occipital lobe | Contralateral hemianopia |
| Lenticulo-striate artery | Internal capsule Striatum | Contralateral paralysis |
| Basilar artery | CN VI Paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) Corticobulbar tract Corticospinal tract | Locked-in syndrome Medial pontine syndrome: Horizontal gaze palsy Pseudobulbar palsy Contralateral paralysis |
| Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) | CN VII & CN VIII Sympathetic fibers Cerebellar peduncles | Lateral pontine syndrome: Ipsilateral facial palsy Ipsilateral deafness Ipsilateral vertigo Ipsilateral Horner syndrome Ipsilateral ataxia |
| Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) | Ambiguous nucleus Sympathetic fibers Cerebellar peduncle Lateral spinothalamic tract | Lateral medullary [Wallenberg] syndrome: Dysphagia Dysarthria ↓ Gag reflex Contralateral palate deviation Ipsilateral Horner syndrome Ipsilateral ataxia Contralateral paresthesia |
| Anterior spinal artery (ASA) | CN XII Corticospinal tract Medial lemniscus | Medial medullary syndrome: Ipsilateral tongue deviation Contralateral paralysis Contralateral paresthesia |
Workup of Ischemic Stroke
- Coagulation panel
- Non-contrast CT of the head
- CT angiography of the head and neck
- MR imaging of the head
- Carotid ultrasound
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Echocardiography
Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
- Antihypertensives
- BP < 185/110 mmHg if revascularization
- BP < 220/120 mmHg otherwise
- Antihyperglycemic if glucose > 140 ~ 180 mg/dL
- Antiplatelets
- Revascularization
- Thrombolysis if duration < 3 ~ 4.5 hours
- Thrombectomy if duration < 6 ~ 24 hours
Ideal Door-to-Reperfusion Time for Ischemic Stroke
- Door-to-needle < 60 minutes
- Door-to-puncture < 120 minutes
Brain Lesions & Breathing Patterns
| Brain Lesion | Breathing Pattern |
|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Cheyne-Stokes respiration |
| Midbrain | Tachypnea |
| Upper pons | Apneustic respiration |
| Lower pons | Cluster respiration |
| Medulla | Ataxic [Biot] respiration |
Abnormal Neurologic Examination Findings in Hemineglect
- Cancellation test
- Reading test
- Bisection of lines
- Copy of drawings
Aphasia
| Aphasia | Comprehension | Repetition | Fluency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Broca | - | ↓ | ↓ |
| Wernicke | ↓ | ↓ | - |
| Conduction | - | ↓ | - |
| Mixed transcortical | ↓ | - | ↓ |
| Transcortical motor | - | - | ↓ |
| Transcortical sensory | ↓ | - | - |
Triad of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH) {3W}
| Mnemonic | Presentation |
|---|---|
| Wet | Urinary incontinence |
| Wobbly | Ataxia |
| Wacky | Cognitive dysfunction |
Presentation of Elevated Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
- Cushing triad
- Pressure :: hypertension & ↑ pulse pressure
- Pulse :: bradycardia
- Respiration :: pattern change
- ↓ Consciousness
- Headache
- Nausea ± vomiting
- Papilledema
- Diplopia
Treatment of Elevated Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
- Position :: head elevation
- Hyperventilation
- Diuretics :: Mannitol
- Sedation
- Corticosteroids
- Craniectomy
Treatment of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)
- Weight loss
- Diuretics
- Acetazolemide
- Loop diuretics
- Topiramate
- Lumbar puncture
- Shunting
- Optic nerve sheath fenestration
Contraindications to Lumbar Puncture
- Skin infection over puncture site
- Brain mass causing ↑ intracranial pressure (ICP)
Types of Primary Headaches
| Cluster | Migraine | Tension | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | Female | - |
| Laterality | Unilateral | Unilateral | Bilateral |
| Location | Periorbital | Head | Band |
| Duration | 15 minutes ~ 3 hours | 4 hours ~ 3 days | 30 minutes ~ 7 days |
| Triggers | - | + | + |
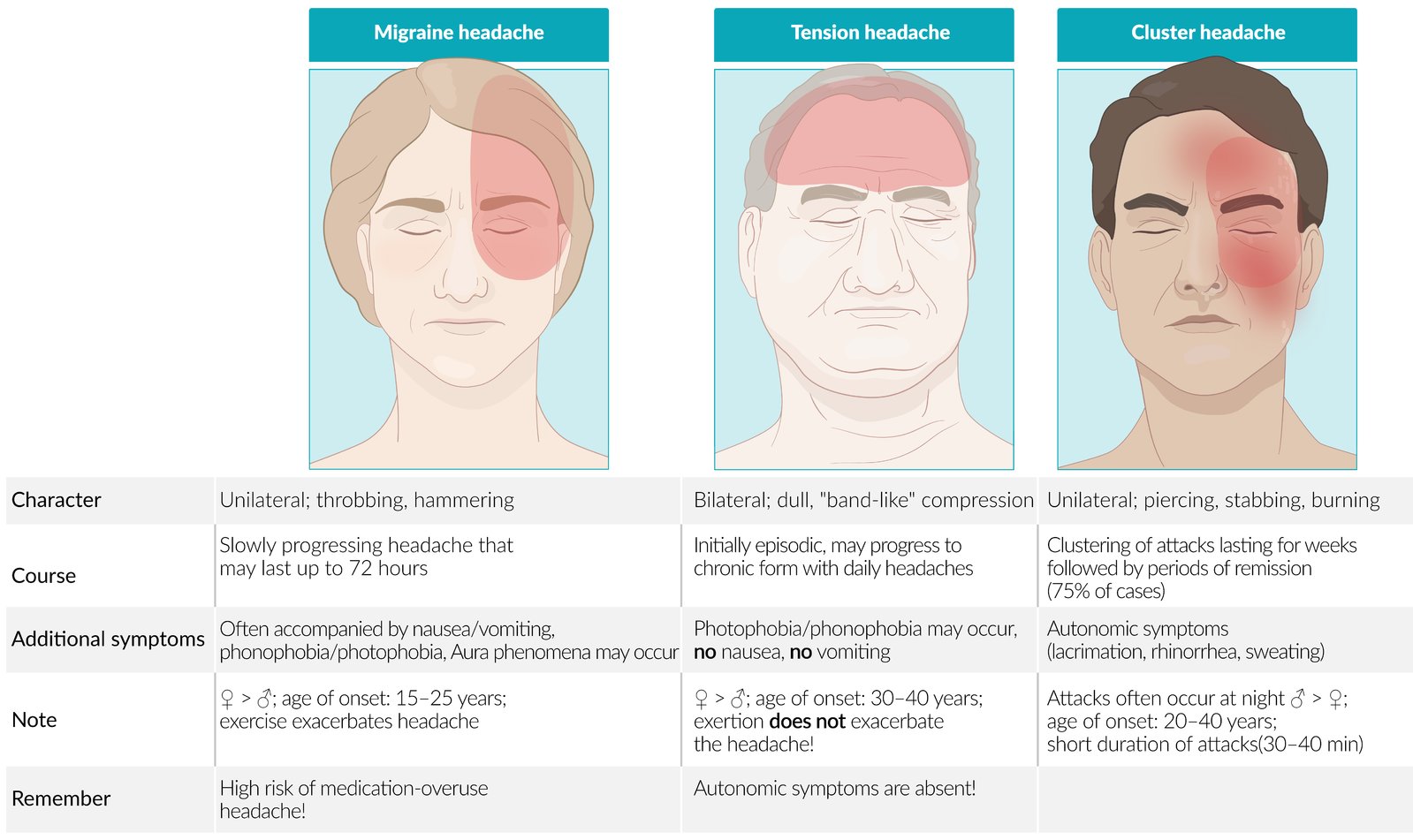
Treatment of Primary Headaches
| Headache | Acute | Chronic |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster | 100% O2 -Triptans | Verapamil |
| Migraine | NSAIDs -Triptans Ergotamine | β antagonists TCAs Valproate Topiramate Botulinum toxin Lifestyle modification |
| Tension | NSAIDs Acetaminophen | TCAs Lifestyle modification |
Red Flags for Secondary Headaches
- Sudden onset
- Onset after 50 y/o
- ↑ frequency or severity
- New onset with an underlying medical condition
- Focal neurologic sequelae
- Papilledema
- Preceding head trauma
Seizures
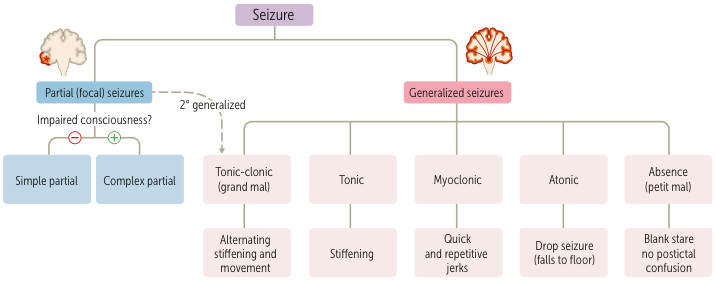
Anticonvulsants
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| Na channel blockers | Phenytoin Valproate Carbamazepine Lamotrigine Topiramate |
| Ca channel blockers | Ethosuximide Gabapentin Pregabalin |
| SV2A antagonists | Levetiracetam |
| GABAA agonists | Barbiturates Benzodiazepines |
| GABA reuptake inhibitors | Tiagabine |
| GABA transaminase inhibitors | Vigabatrin |
Treatment of Status Epilepticus
- Barbiturates
- Benzodiazepines
- Phenytoin
Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
- Ca channel blockers
- Gabapentin
- Pregabalin
- Reuptake inhibitors
- TCAs
- SNRIs
Treatment of Essential Tremor
- β antagonists :: Propranolol
- Barbiturates :: Primidone
Neurodegenerative Disorders
| Disorder | Lesions | Findings | Precursor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinson disease | Substantia nigra | Lewy body | α-Synuclein |
| Huntington disease | Striatum | - | - |
| Alzheimer disease | Cortex Hippocampus | Senile plaque | Amyloid precursor protein (APP) |
| Neurofibrillary tangle | Tau protein | ||
| Hirano body | Actin | ||
| Frontotemporal dementia | Frontotemporal lobe | Pick body | Tau protein |
| Lewy body dementia | Cortex | Lewy body | α-Synuclein |
| Vascular dementia | Cortex | - | - |
| Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) | - | - | - |
| Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease | Striatum | Prion | Prion protein (PrP) |
Basal Ganglia and Diseases
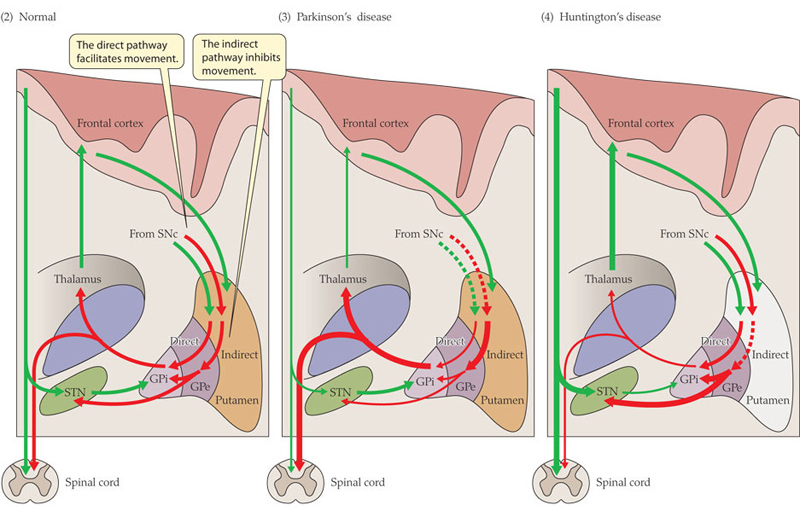
Presentation of Parkinson Disease {PARTS}
- Postural instability
- Akinesia & Bradykinesia
- Rigidity :: cogwheel
- Tremor :: resting & pill-rolling
- Shuffling gait
Medications for Parkinson Disease
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| M antagonists | Benztropine |
| D2 agonists | Bromocriptine Cabergoline Pramipexole Ropinirole |
| MAO inhibitors | Selegiline |
| COMT inhibitors | -Capones |
| Dopa | Levodopa |
| Dopa decarboxylase inhibitors | Carbidopa Benserazide |
| NMDA antagonists | Amantadine |
Treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
- Ca channel blockers
- Gabapentin
- Pregabalin
- Levodopa
- D2 agonists
- Pramipexole
- Ropinirole
Medications for Huntington Disease
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| VMAT2 inhibitors | Tetrabenazine Valbenazine |
| D2 antagonists | 2° Antipsychotics |
Medications for Alzheimer Disease
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| ACh esterase inhibitors | Rivastigmine Galantamine Donepezil |
| NMDA antagonists | Memantine |
Etiology of Myelopathy
| Lesion | Dorsal Column | Spinothalamic Tract | Corticospinal Tract | Anterior Horn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syringomyelia | - | - | - | - |
| Poliomyelitis | - | - | - | + |
| Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) | - | - | - | + |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | - | - | + | + |
| Tabes dorsalis | + | - | - | - |
| Subacute combined degeneration (SCD) | + | - | + | - |
| Anterior spinal artery syndrome | - | + | + | + |
| Brown-Sequard syndrome | + | + | + | + |
| Transverse myelopathy | + | + | + | + |
Etiology of Peripheral Neuropathy
- Heme synthesis disorders
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Chemotherapy toxicity
- Tabes dorsalis
- Subacute combined degeneration (SCD)
- Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS)
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease
Demyelinating Diseases
- Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- Leukodystrophies
- Tabes dorsalis
- Subacute combined degeneration (SCD)
- Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS)
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease
Charcot Triad of Multiple Sclerosis {SIN}
- Scanning speech
- Intention tremor
- Incontinence
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia
- Nystagmus
White Matters Affected By Multiple Sclerosis
| White Matter | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Optic nerve | Marcus Gunn pupil |
| Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) | Internuclear ophthalmoplegia Nystagmus |
| Cerebellum | Scanning speech Intention tremor |
| Spinal cord | Incontinence |
Types of Multiple Sclerosis
- Relapsing-remitting
- Progressive relapsing
- 1° progressive
- 2° progressive
Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| NF-κB inhibitors | Corticosteroids |
| CD20 inhibitors | Ocrelizumab |
| CD52 inhibitors | Alemtuzumab |
| α4-integrin inhibitors | Natalizumab |
| - | Plasmapheresis |
| - | IFN-β |
Treatment of Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS)
- Plasmapheresis
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
Comparison Between UMN and LMN Lesions
| UMN | LMN | |
|---|---|---|
| Weakness | + | + |
| Atrophy | - | + |
| Fasciculations | - | + |
| Tone | ↑ | ↓ |
| Reflexes | ↑ | ↓ |
| Primitive reflexes | + | - |
| Paralysis | Spastic | Flaccid |
- Upper motor neuron (UMN)
- Lower motor neuron (LMN)
Abnormal Physical Examination Findings in Nerve Injuries
| Exam | Injury |
|---|---|
| Lhermitte sign | Cervical myelopathy |
| Spurling test | Cervical radiculopathy |
| Kemp test | Lumbar radiculopathy |
| Straight leg raising test (SLRT) | Lumbar radiculopathy |
| Hoffmann sign | UMN lesion |
| Babinski sign | UMN lesion |
Evoked Electromyography (EMG)
.png)
Interpretation of Electromyograghy (EMG)
| Condition | Rest | Amplitude | Duration | Phase | Recruitment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | - | 0.2 ~ 2 mV | 5 ~ 15 ms | Triphasic | - |
| Neuropathy :: UMN | - | - | - | Triphasic | - |
| Neuropathy :: LMN | Fibrillations | ↑ | ↑ | Polyphasic | ↓ |
| Myopathy :: non-inflammatory | - | ↓ | ↓ | Polyphasic | ↑ |
| Myopathy :: inflammatory | Fibrillations | ↓ | ↓ | Polyphasic | ↑ |
Etiology of Myopathy
- Inflammatory myopathy
- Polymyositis
- Dermatomyositis
- Endocrine
- Hypothyroidism
- Cushing syndrome
- Metabolic myopathy
- Glycogen storage diseases (GSD)
- Lysosomal storage diseases (LSD)
- Muscular dystrophy
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy
- Drug-induced myopathy
- Rhabdomyolysis
Comparison Between Myopathy and Myalgia
| Myopathy | PMR | Fibromyalgia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESR | ↑/- | ↑ | - |
| CK | ↑ | - | - |
Pathogenesis of Horner Syndrome
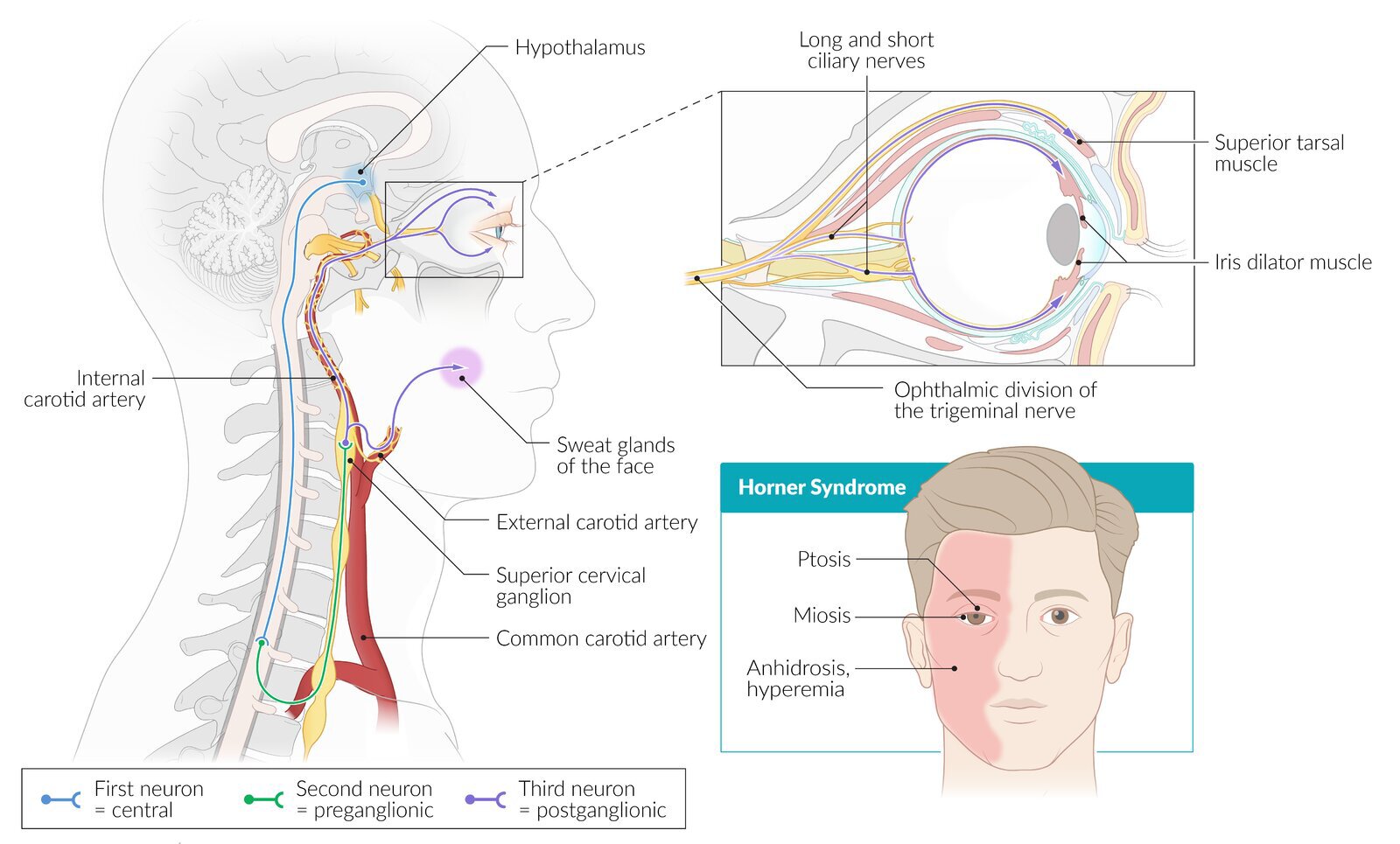
Etiology of Horner Syndrome
- Ischemic stroke
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
- Pancoast tumor
- Carotid dissection
Presentation of Horner Syndrome {MAP}
- Miosis
- Anhidrosis
- Ptosis :: superior tarsal muscle
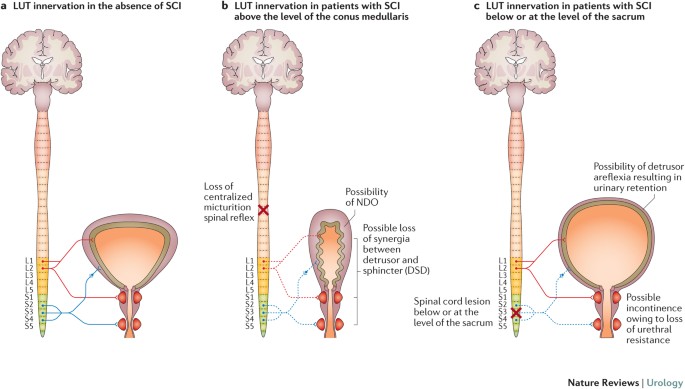
Etiology of Neurogenic Bladder
- Stroke
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Neurodegenerative disorders
- Cauda equina syndrome
- Herniated disk
- Spinal cord injury
- Spinal stenosis
- Diabetic neuropathy
CSF Analysis
| Pressure | WBCs | Glucose | Protein | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 50 ~ 180 mmH2O | < 5/mm3 | 40 ~ 70 mg/dL | 20 ~ 45 mg/dL |
| Inflammatory | - | - | - | ↑ |
| Bacterial | ↑ | ↑ PMNs | ↓ | ↑ |
| TB & Fungal | ↑ | ↑ Lymphocytes | ↓ | ↑ |
| Viral | ↑ | ↑ Lymphocytes | - | ↑ |
IgG Index
| Parameter | (CSFIgG ÷ CSFAlbumin) ÷ (PIgG ÷ PAlbumin) |
|---|---|
| CSFIgG | CSF IgG |
| CSFAlbumin | CSF albumin |
| PIgG | Serum IgG |
| PAlbumin | Serum albumin |
Routes of Brain Abscess Transmission
- Hematogenous spread
- Direct spread
- Paranasal sinusitis
- Otitis media
- Mastoiditis
- Dental infection
- Direct innoculation
Pathogens of Encephalitis
- Arbovirus
- Enterovirus
- HSV
- VZV
- CMV
- Toxoplasmosis
- Malaria
Pathogens of Meningitis
- Streptococcus pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Neisseria meningitidis
- Enterovirus
- HSV & HIV
- Cryptococcus
Empirical Antibiotics for Meningitis
| Patient | Antibiotics |
|---|---|
| ≤ 1 month | Ampicillin & (3° Cephalosporins / Aminoglycosides) |
| 1 ~ 3 months | Vancomycin & 3° Cephalosporins |
| 3 months ~ 60 years | Vancomycin & 3° Cephalosporins |
| ≥ 60 years Complicated | Vancomycin & Ampicillin & 3° Cephalosporins |
Nervous System Tumors
Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumors
| Cell | Origin | Tumors |
|---|---|---|
| Neurons | Neural tube | Neuroblastoma |
| Astrocytes | Neural tube | Astrocytoma |
| Ependymal cells | Neural tube | Ependymoma |
| Oligodendrocytes | Neural tube | Oligodendroglioma |
| Neuroendocrine cells | Neural tube | Pinealoma |
| Neuroendocrine cells | Surface ectoderm | Craniopharyngioma Pituitary adenoma |
| Meninges | Neural crest | Meningioma |
| Microglia | Mesoderm | - |
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Tumors
| Cell | Origin | Tumors |
|---|---|---|
| Neurons | Neural crest | Ganglioneuroma Neuroblastoma |
| Schwann cells | Neural crest | Schwannoma Neurofibroma Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) |
| Neuroendocrine cells | Neural crest | Pheochromocytoma Paraganglioma |
WHO Grading of Astrocytoma
| Grade | Tumor |
|---|---|
| 1 | Pilocytic astrocytoma |
| 2 | Fibrillary astrocytoma |
| 3 | Anaplastic astrocytoma |
| 4 | Glioblastoma multiforme |
Pathological Workup of Meningioma
- Mitotic index
- Brain invasion
- Atypical features
- Necrosis
- Sheeted architecture
- Small cell change
- Hypercellularity
- Macronuclei
Management of Pituitary Adenoma
| Condition | Management |
|---|---|
| Prolactinoma | Pharmacotherapy |
| Non-PRL secretory | Surgery |
| Non-secretory | Surgery |
| Asymptomatic | Observation |
Disorders of Consciousness
| Awareness | SWC | BR | SR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain death | - | - | - | - |
| Coma | - | - | + | + |
| Vegetative state | - | + | + | + |
| Minimally conscious state | ± | + | + | + |
| Locked-in syndrome | + | + | + | + |
- Sleep-wake cycle (SWC)
- Brainstem reflex (BR)
- Spontaneous respiration (SR)
Neurologic Examination for Brain Death
- Posturing
- Pupillary reflex
- Corneal reflex
- Vestibulo-ocular reflex
- Gag reflex
- Cough reflex
Indications for Polysomnography
- Sleep apnea
- Sleep-wake disorders
Triad of Anesthesia
- Hypnosis
- Analgesia
- Muscle relaxation
Medications for General Anesthesia
| Mechanism | Medication | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| GABAA agonists | Barbiturate | Anesthesia :: intravenous |
| Benzodiazepine | Anesthesia :: intravenous | |
| Propofol | Anesthesia :: intravenous | |
| Etomidate | Anesthesia :: intravenous | |
| NMDA antagonists | Ketamine | Anesthesia :: intravenous |
| ↓ CNS | Nitrous oxide (N2O) | Anesthesia :: inhalational |
| Halothane | Anesthesia :: inhalational | |
| Desflurane | Anesthesia :: inhalational | |
| Enflurane | Anesthesia :: inhalational | |
| Isoflurane | Anesthesia :: inhalational | |
| Sevoflurane | Anesthesia :: inhalational |
Contraindications to Neuraxial Blockade {CHIPS}
- Coagulopathy
- Hypovolemia
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Infection
- Patient refusal
- Stenosis :: mitral valve & aortic valve
Order of Nerve Blockade
- Small myelinated fibers
- Small unmyelinated fibers
- Large myelinated fibers
- Large unmyelinated fibers
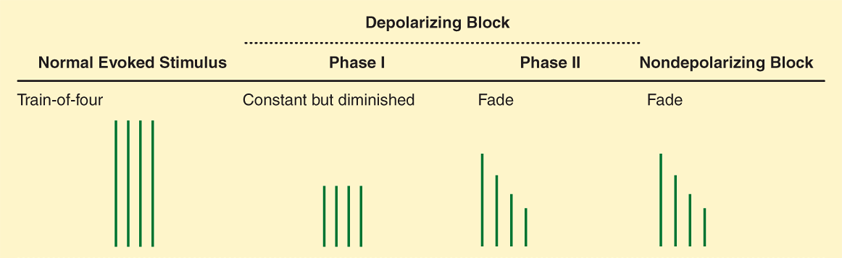
Neuromuscular Blockade