Respiratory System
Abnormal Ventilation/Perfusion (V/Q) Ratio
Shunt [↓ V/Q]
- Anatomic shunt
- Intracardiac shunt
- Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- Physiologic shunt
- Obstructive lung diseases
- Alveolar lung diseases
Dead Space [↑ V/Q]
- Shock
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary vascular diseases
Etiology of Increased A-a Gradient
- Interstitial lung diseases
- V/Q mismatch
Etiology of Hypoventilation
- ↓ Respiratory drive
- ↓ Tidal volume
- Neuromuscular disorders
- Chest wall deformities
Abnormal Physical Examination Findings
| Finding | Mechanism | Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperresonant percussion | ↓ Density | Pneumothorax Emphysema |
| Dull percussion | ↑ Density | Pleural effusion Lung consolidation |
| ↓ Fremitus | Accumulation in pleural space | Pleural effusion |
| ↑ Fremitus | Accumulation in lung | Lung consolidation |
Abnormal Breathing Patterns
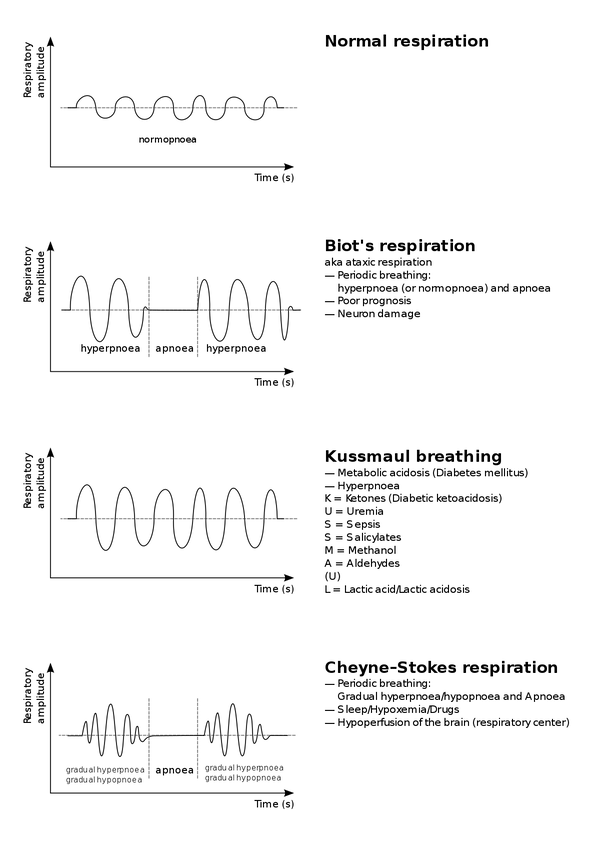
Etiology of Kussmaul Breathing {KUSSMAUL}
- Ketoacidosis
- Uremia
- Sepsis
- Salicylate
- Methanol
- Aldehyde
- Uricemia
- Lactic acidosis
Etiology of DLCO Changes
Decreased DLCO
- Emphysema
- Interstitial lung diseases
Increased DLCO
- Asthma
Light Criteria for Pleural Fluid (PF)
| PF | PF ÷ Serum TP | PF ÷ Serum LDH | PF LDH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transudate | < 0.5 | < 0.6 | < 2/3 Serum LDH upper limit |
| Exudate | > 0.5 | > 0.6 | > 2/3 Serum LDH upper limit |
- Total protein (TP)
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Comparison Between Obstructive and Restrictive Lung Diseases
| Obstructive | Restrictive | |
|---|---|---|
| TLC | ↑ | ↓ |
| FEV1 | ↓ | ↓ |
| FVC | - | ↓ |
| FEV1/FVC | ↓ | - |
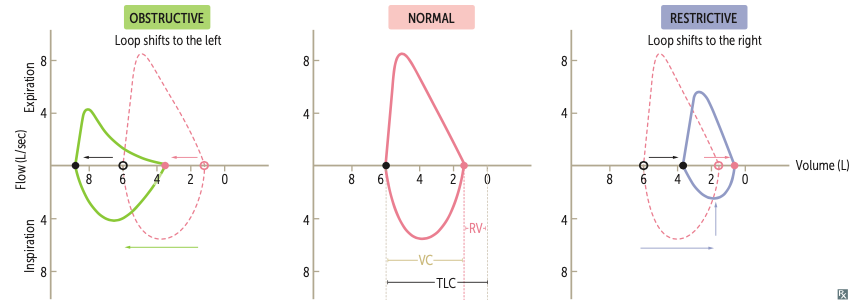
Types of Obstructive Lung Diseases
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Chronic bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Centriacinar emphysema
- Panacinar emphysema
- Bronchiectasis
- Central bronchiectasis
- Peripheral bronchiectasis
Etiology of Obstructive Lung Diseases
| Disease | Etiology |
|---|---|
| Asthma | Hypersensitivity |
| Chronic bronchitis | Smoking |
| Centriacinar emphysema | Smoking |
| Panacinar emphysema | α1-antitrypsin deficiency |
| Central bronchiectasis | Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) |
| Peripheral bronchiectasis | Cystic fibrosis Primary ciliary dyskinesia Immunodeficiency |
Classification of Asthma Severity
| Asthma | Attacks | Awakenings | SABA Uses | FEV1 | FEV1/FVC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermittent | < 2 days/week | ≤ 2/month | ≤ 2 days/week | > 80% | Normal |
| Mild persistent | 2 ~ 7 days/week | 3 ~ 4/month | 2 ~ 7 days/week | > 80% | Normal |
| Moderate persistent | Daily | > 1/week | Daily | 60 ~ 80% | ↓ < 0.05 |
| Severe persistent | Throughout | Daily | Throughout | < 60% | ↓ > 0.05 |
Medications for Asthma
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| β2 agonists | Albuterol Salmeterol Formoterol |
| M antagonists | Ipratropium Tiotropium |
| NF-κB inhibitors | Corticosteroids |
| LOX inhibitors | Zileuton |
| LTD4 antagonists | Montelukast Zafirlukast |
| Mast cell inhibitors | Cromolyn Nedocromil |
| IgE inhibitors | Omalizumab |
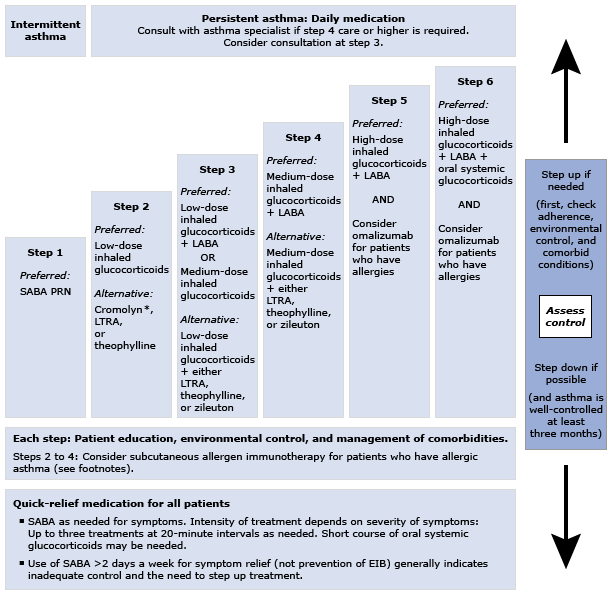
Treatment of Asthma
Acute Asthma
- Nebulized β2 agonists
- Intravenous magnesium
- Intravenous corticosteroids
Chronic Asthma
GOLD Staging of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
| Stage | Severity | FEV1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mild | > 80% |
| 2 | Moderate | 50 ~ 80% |
| 3 | Severe | 30 ~ 50% |
| 4 | Very severe | < 30% |
Types of Pneumoconioses
| Type | Deposit | Location | Findings | Associations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asbestosis | Asbestos | Lung base | Calcified pleural plaques Ferruginous bodies | Bronchogenic carcinoma Mesothelioma |
| Coal worker's disease | Coal dust | Lung apex | - | - |
| Silicosis | Silica | Lung apex | Eggshell calcifications | Tuberculosis |
| Berylliosis | Beryllium | Hilum | Hilar adenopathy | - |
Types of Lung Cancers
| Type | Location | Paraneoplastic Syndromes |
|---|---|---|
| Small cell carcinoma | Central | ACTH & SIADH Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome Paraneoplastic myelitis/encephalitis |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Central | PTHrP |
| Adenocarcinoma | Peripheral | - |
| Large cell carcinoma | Peripheral | β-hCG |
Modified Wells Criteria for Pulmonary Embolism
| Criteria | Points |
|---|---|
| DVT symptoms/signs | 3 |
| Clinical suspicion | 3 |
| Tachycardia | 1.5 |
| Immobilization | 1.5 |
| Previous PE/DVT | 1.5 |
| Hemoptysis | 1 |
| Malignancy | 1 |
Management of Suspected Pulmonary Embolism
| Score | Risk | Management |
|---|---|---|
| 0 ~ 1 | Low | D-dimer |
| 2 ~ 6 | Intermediate | CT angiography V/Q scan Bedside echocardiography |
| ≥ 7 | High | Treatment |
Evaluation for Pulmonary Embolism
- D-dimer
- CT angiography
- Ventilation/Perfusion (V/Q) scan
- Bedside echocardiography
Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
- Anticoagulants
- IVC filter
- Revascularization
- Thrombolysis
- Thrombectomy
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
| Infection | Pathogens | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Epiglottitis | Haemophilus influenzae | Antibiotics Intubation |
| Laryngotracheobronchitis [Croup] | Parainfluenza virus | Corticosteroids Nebulized epinephrine |
| Bronchitis Bronchiolitis | Virus | Supportive care |
| Pneumonia | Any | Antimicrobials |
Sputum Sample Acceptable for Gram Stain
- PMNs > 25/HPF
- Epithelial cells < 10/HPF
Pathogens of Bronchitis & Bronchiolitis
- RSV
- Rhinovirus
- Parainfluenza virus
- Influenza virus
- Adenovirus
- Coronavirus
Pathogens of Pneumonia
Lobar Pneumonia & Bronchopneumonia
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Anaerobes
- Virus
Atypical Pneumonia {LCM}
- Legionella
- Chlamydia
- Mycoplasma
Phases of Pneumonia
- Congestion
- Red hepatization
- Grey hepatization
- Resolution
Empirical Antibiotics for Pneumonia
| Patient | Antibiotics |
|---|---|
| CAP & Outpatient | Amoxicillin Macrolides / Doxycycline |
| CAP & Outpatient & Complicated | Amoxicillin & (Macrolides / Doxycycline) Fluoroquinolones |
| CAP & Inpatient | Anti-pneumococcal β-lactams & (Macrolides / Doxycycline) Fluoroquinolones |
| CAP & Inpatient & Complicated | Anti-pneumococcal β-lactams & Fluoroquinolones |
| HAP | Anti-MRSA & Anti-pseudomonal β-lactams & Fluoroquinolones |
Complicated Outpatients
- Age > 65 years
- Antibiotics within 3 months
- Commorbid
CURB-65 Score for Inpatient
- Confusion
- Uremia :: BUN > 19
- Respiratory rate > 30
- Blood pressure :: SBP/DBP < 90/60 mm Hg
- Age > 65 years
Respiratory Failure
| Type | PaO2 | PaCO2 | A-a Gradient | Etiology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ↓ | - | ↑ | V/Q mismatch |
| 2 | ↓ | ↑ | - | Hypoventilation |
| 3 | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | Mixed |
| 4 | ↓ | ↑ | - | Sepsis |
Indications for Mechanical Ventilation
- GCS ≤ 8
- PaCO2 > 50 mmHg
- PaO2 < 60 mmHg
- SpO2 < 90%
Ventilator Modes
| Sequence | Control | Trigger | Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous mandatory | Presure (PC) Volume (VC) | Time | Assist-control ventilation (ACV) |
| Intermittent mandatory | Presure (PC) Volume (VC) | Time Patient | Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) |
| Continuous spontaneous | - | Patient | Pressure support ventilation (PSV) |
Etiology of Post-intubation Desaturation {DOPE}
- Displacement
- Obstruction
- Pneumothorax
- Equipment failure
Ventilation Weaning Parameters
| Parameter | Normal Adult Range | Weaning Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Rate (RR) | 14 ~ 18 | < 40 |
| Tidal Volume (VT) | 5 ~ 7 mL/kg | 5 mL/kg |
| Rapid shallow breathing index (RSBI) = RR ÷ VT | < 50/min/L | < 105/min/L |
| PF Ratio = PaO2 ÷ FiO2 | > 400 | > 200 |
| Max Inspiratory Pressure | < -90 cm H2O | < -25 cm H2O |