Medicine
Core Ethical Principles
| Mnemonic | Principle |
|---|---|
| Just | Justice |
| Always | Autonomous |
| Be | Beneficence |
| Nice | Nonmaleficence |
Differential Diagnosis {VINDICATE}
- Vascular
- Infection & Inflammation
- Neoplasia & Nutrition
- Degeneration & Drugs
- Idiopathic
- Congenital
- Autoimmunity
- Trauma & Toxins
- Endocrine & Exocrine
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) {DEATH}
- Dressing
- Eating
- Ambulating
- Toileting
- Hygiene
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Scale
%20Performance%20Scale.png)
Evaluation of Family Function {APGAR}
- Adaptability
- Partnership
- Growth
- Affection
- Resolve
Lethal Triad {CAH}
- Coagulopathy
- Acidosis
- Hypothermia
Leading Causes of Death in General Population
- Heart :: cardiovascular disease
- Cancer
- Lung :: chronic respiratory disease
- Brain :: cerebrovascular disease
- Accident
Leading Causes of Death in Newborns
- Congenital anomalies
- Small for gestational age (SGA)
- Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
Risk Factors for Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Maternal Factors
- Substance use
- Age < 20 years
Infant Factors
- Prematurity
- Low birth weight
- Sleep environment
- Smoke exposure
Complications of Prematurity
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
- Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS)
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
- Cerebral palsy
- Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH)
- Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL)
- Retinopathy of prematurity
Complications of Postmaturity
- Macrosomia
- Oligohydramnios
- Hypoglycemia
- Polycythemia
- Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS)
- Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN)
Classification of Birth Weights (BW)
| Classification | BW (g) |
|---|---|
| Extremely low (ELBW) | < 1000 |
| Very low (VLBW) | 1000 ~ 1500 |
| Low (LBW) | 1500 ~ 2500 |
| Normal (NBW) | 2500 ~ 4000 |
| High (HBW) | > 4000 |
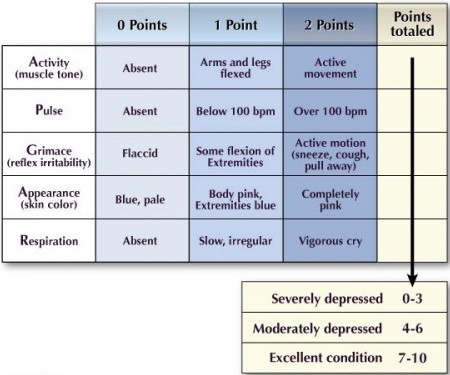
Apgar Score
New Ballard Score {HAPPSS}
- Heel to ear
- Arm recoil
- Popliteal angle
- Posture
- Scarf sign
- Square window
Contraindications to Breastfeeding
- Galactosemia
- HIV
- HSV on breasts
- Tuberculosis
- Sepsis
- Chemotherapy
- Substance use
Conditions Associated with Enlarged Anterior Fontanel
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Rickets
- Achondroplasia
- Elevated intracranial pressure (ICP)
VACTERL Association {VACTERL}
- Vertebral anomalies
- Anorectal malformation
- Cardiac anomalies :: ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF)
- Esophageal atresia (EA)
- Renal anomalies
- Limb anomalies
Presentation of Potter Sequence {POTTER}
- Pulmonary hypoplasia
- Oligohydramnios
- Twisted face
- Twisted skin
- Extremity defects
- Renal failure
Primary Survey for Trauma {ABCDE}
- Airway
- Breathing
- Circulation
- Disability
- Exposure
Presentation of Non-accidental Trauma (NAT)
- Burns
- Fractures
- Rib fractures
- Corner [Bucket handle] fractures
- Spiral fractures
- Hemorrhage
- Subdural hemorrhage
- Retinal hemorrhage
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Levels of Consciousness {ALOSC}
- Alert
- Lethargic
- Obtunded
- Stuporous
- Comatose
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Eye Opening
| Item | Score |
|---|---|
| Spontaneous | 4 |
| Respond to command | 3 |
| Respond to pain | 2 |
| Absent | 1 |
Verbal Response
| Item | Score |
|---|---|
| Oriented | 5 |
| Confused | 4 |
| Inappropriate | 3 |
| Incomprehensible | 2 |
| Absent | 1 |
Motor Response
| Item | Score |
|---|---|
| Obedient | 6 |
| Localization of pain | 5 |
| Withdrawal from pain | 4 |
| Flexion to pain | 3 |
| Extension to pain | 2 |
| Absent | 1 |
Etiology of Altered Mental Status (AMS) {AEIOU-TIPS}
- Acidosis
- Electrolyte disturbances
- Intoxication
- Oxygen
- Uremia
- Trauma
- Infection
- Psychosis
- Sugar
- Seizures
- Strokes
- Syncope
Coma Cocktail {DONT}
- Dextrose
- Oxygen
- Naloxone
- Thiamine
Etiology of Syncope
- Orthostatic
- Cardiac
- Neurologic
- Reflex
- Vasovagal [Neurocardiogenic]
- Situational
- Psychogenic
Etiology of Fever
- Infection
- Neoplasm
- Autoimmunity
- Drugs
- Endocrine
Workup of Fever
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Throat swab ± Sputum culture
- Chest radiography
- Urinalysis ± Urine culture
- Wound inspection
Grading of Pitting Edema
| Grade | Depth | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 mm | ≤ 2 seconds |
| 2 | 4 mm | 2 seconds ~ 1 minute |
| 3 | 6 mm | 1 ~ 2 minutes |
| 4 | 8 mm | ≥ 2 minutes |
Classification of Edema
| Edema | Etiology | Pitting |
|---|---|---|
| Exudate | Inflammation | + |
| Transudate | Hydrostatic pressure | + |
| Oncotic pressure | + | |
| Lymphedema | Lymphatic obstruction | - |
Grading of Peripheral Pulses
| Grade | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Absent |
| 1 | Diminished |
| 2 | Normal |
| 3 | Increased |
| 4 | Bounding |
Etiology of Cardiopulmonary Arrest {5H5T}
- Hypothermia
- Hypovolemia
- Hypoxia
- Hydrogen
- Hypokalemia & Hyperkalemia
- Tamponade
- Tension pneumothorax
- Thrombosis :: myocardial infarction
- Thrombosis :: pulmonary embolism
- Toxins
Blood Pressure
| Condition | Definition |
|---|---|
| Hypotension | < 90/60 mmHg |
| Hypertension | > 140/90 mmHg |
| Hypertensive urgency | > 180/120 mmHg |
Classification of Shock
| Shock | PCWP | CO | SVR | MAP | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypovolemic | ↓ (1°) | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | Fluids |
| Cardiogenic | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↑ | ↓ | Inotropes Diuretics Venodilators |
| Distributive | - | ↑ | ↓ (1°) | ↓ | Vasopressors |
Types of Distributive Shock
- Anaphylactic shock
- Septic shock
- Neurogenic shock
Classification of Hypovolemic Shock
| Class | Loss | HR | BP | RR | Urine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | < 15% | < 100 | - | 12 ~ 20 | > 30 mL/h |
| II | 15 ~ 30% | 100 ~ 120 | - | 20 ~ 30 | 20 ~ 30 mL/h |
| III | 30 ~ 40% | 120 ~ 140 | ↓ | 30 ~ 40 | 5 ~ 15 mL/h |
| IV | > 40% | > 140 | ↓ | > 35 | < 5 mL/h |
Management of Hypertension
Hypertensive Urgency
- ACEI :: Captopril
- β1 antagonists :: Labetalol
- Venodilators & Vasodilators
- Ca channel blockers
- α2 agonists
- Nitrates
Hypertension {ABVD}
- ACEI & ARB
- β1 antagonists
- Vasodilators
- Diuretics
Etiology of Dyspnea
- Anemia
- Hemoglobinopathy
- ↓ Tidal volume
- V/Q mismatch
- Psychological
Etiology of Hypoxemia [↓ PaO2]
- PaCO2 :: normal
- A-a gradient :: normal [Low FiO2]
- A-a gradient :: high
- O2 :: uncorrectable [Shunt]
- O2 :: correctable
- V/Q :: normal [Diffusion limitation]
- V/Q :: mismatch [Dead space]
- PaCO2 :: high [Hypoventilation]
Etiology of Hypercapnia [↑ PaCO2]
- Hypoventilation
- Severe V/Q mismatch
Etiology of Elevated LDH
- Hemolytic anemia
- Germ cell tumors
- Tumor lysis syndrome
Pain Relieved By Leaning Forward
- Pericarditis
- Pancreatitis
Routine Health Maintenance Screening
| Disease | Population | Age (years) | Tests | Interval (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV | All | 15 ~ 65 | - | Once |
| Hypertension | All | All | - | 2 |
| Hyperlipidemia | Male | > 35 | - | Once |
| Female | > 45 | - | Once | |
| Diabetes | All | > 45 | FBG | Once |
| AAA | Male smoker | 65 ~ 75 | Ultrasound | Once |
| Osteoporosis | Female | > 65 | DEXA | 2 |