Pathology
Cell Adaptation
| Type | Size | Number | MC | FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atrophy | ↓ | - | - | - |
| Hypertrophy | ↑ | - | - | - |
| Dystrophy | - | - | + | + |
| Aplasia | - | ↓ | - | - |
| Hypoplasia | - | ↓ | - | - |
| Hyperplasia | - | ↑ | - | - |
| Neoplasia | - | ↑ | - | - |
| Metaplasia | - | - | + | + |
| Dysplasia | - | - | + | + |
- Morphological change (MC)
- Functional change (FC)
Metaplasia
| Organ | Normal | Metaplasia | Stimulus | Disease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airways | Pseudostratified columnar epithelium | Squamous epithelium | Cigarette | Lung SCC |
| Esophagus | Squamous epithelium | Columnar epithelium | Low pH & GERD | Esophageal adenocarcinoma |
| Urinary bladder | Transitional epithelium | Squamous epithelium | Bladder stone | Bladder SCC |
| Endocervix | Columnar epithelium | Squamous epithelium | Low pH | Cervical SCC |
| Muscle | Muscle | Bone | Trauma | Myositis ossificans |
Cell Necrosis
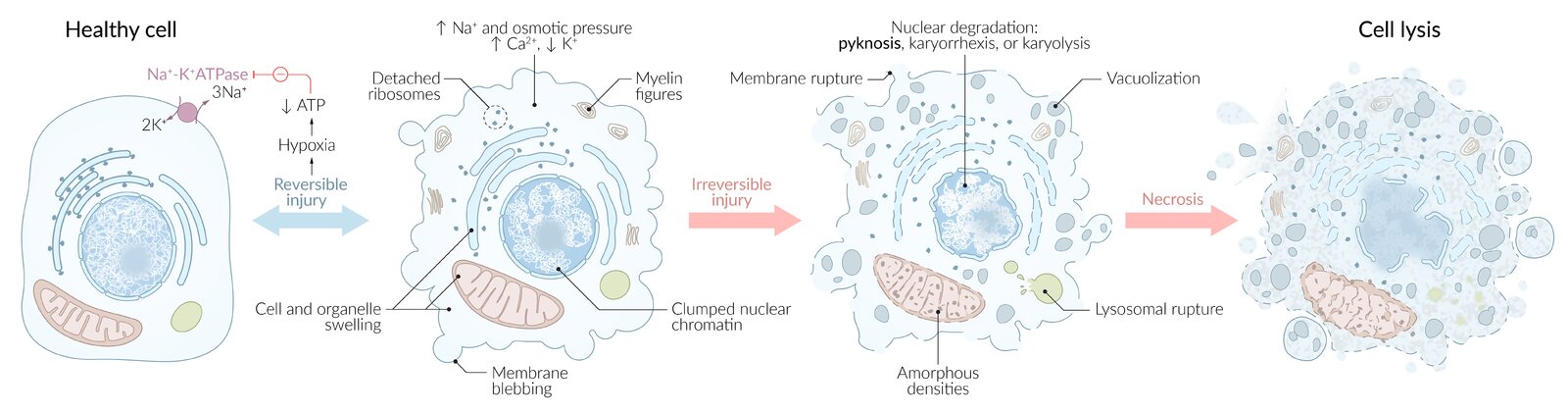
Tissue Necrosis
| Tissue | Infection | Non-infection |
|---|---|---|
| General | Liquefactive Caseous | Coagulative |
| Brain | Liquefactive | Liquefactive |
| Blood vessel | Fibrinoid | Fibrinoid |
| Fat | Fatty | Fatty |
| Limbs GI tract | Wet gangrene | Dry gangrene |
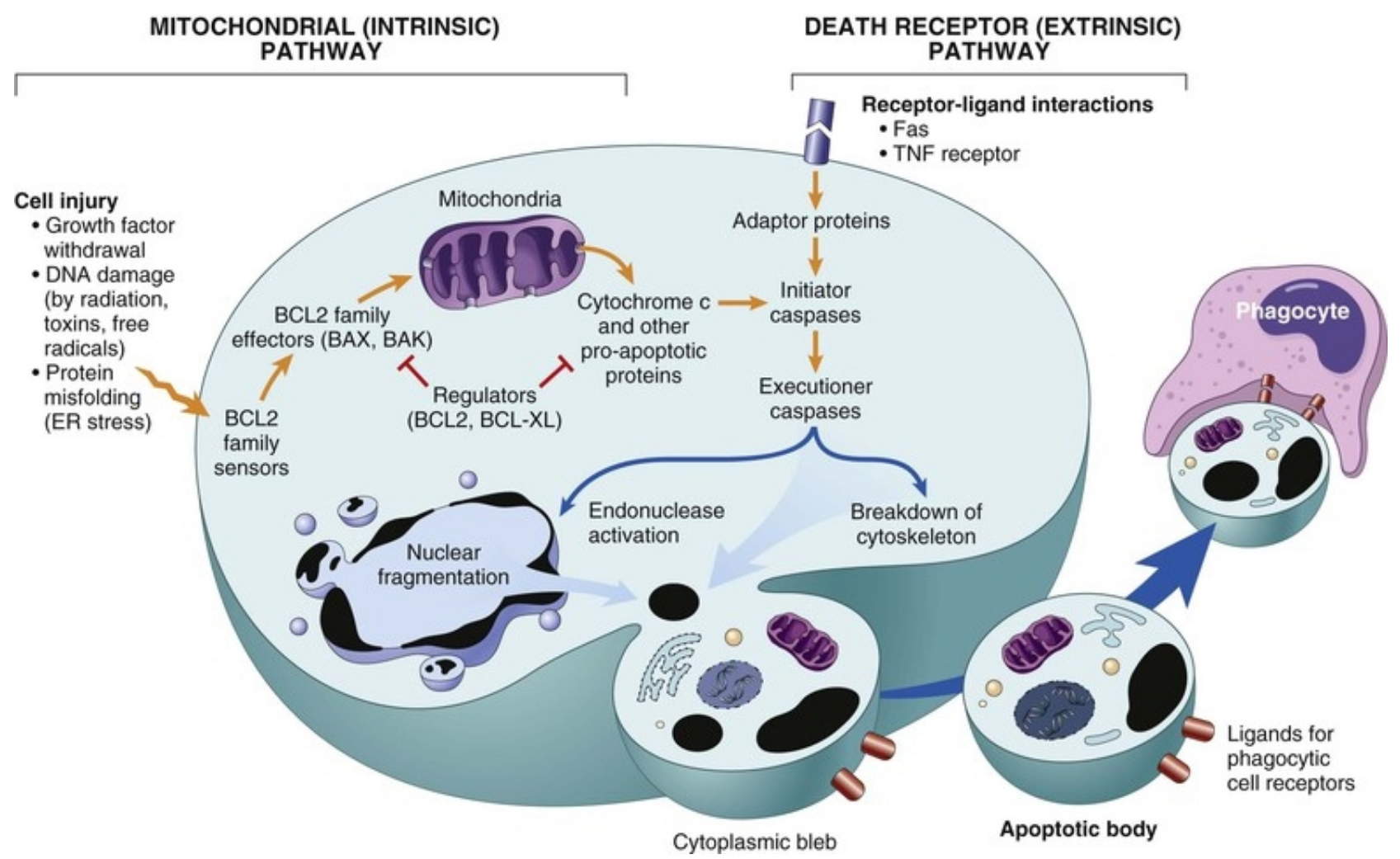
Pathways of Apoptosis
- Mitochondrial [Intrinsic] pathway
- Death receptor [Extrinsic] pathway
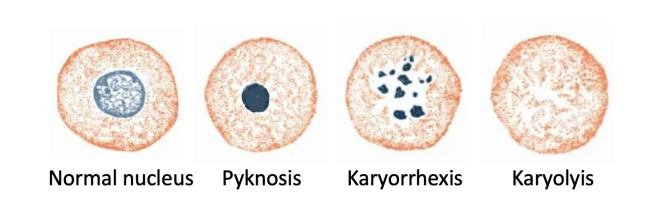
Nuclear Changes in Cell Death
- Pyknosis
- Karyorrhexis
- Karyolysis
Pathological Findings
| Finding | Ingredients | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Anitschkow cell Aschoff body | Macrophage | Rheumatic fever |
| Asteroid body Schaumann body | Calcium Protein | Sarcoidosis |
| Auer body | Peroxidase | AML M3 |
| Basophilic stippling | Ribosomes | Sideroblastic anemia |
| Call-Exner body | - | Granulosa cell tumor |
| Charcot-Leyden crystal | Eosinophil | Asthma |
| Clue cell | Gardnerella vaginalis | Gardnerella vaginalis |
| Cowdry type A | HSV & VZV | HSV & VZV |
| Cowdry type B | Poliovirus Adenovirus | Poliovirus Adenovirus |
| Curschmann spirals | Epithelium | Asthma |
| Ferruginous body | Asbestos | Asbestosis |
| Foam cell | Lipid | Atherosclerosis |
| Gaucher cell | Glucocerebroside | Gaucher disease |
| Giant cell | Macrophage | Granuloma |
| Heart failure cell | Hemosiderin | Left heart failure |
| Heinz body | Hemoglobin | G6PD deficiency |
| Hirano body | Actin | Alzheimer disease |
| Howell-Jolly body | Nuclear remnants | Asplenia |
| Hurthle cell | - | Hashimoto thyroiditis |
| Lewy body | α-Synuclein | Parkinson disease Lewy body dementia |
| Mallory body | Keratin | Alcoholic hepatitis |
| Negri body | Rabies | Rabies |
| Neurofibrillary tangle | Tau protein | Alzheimer disease |
| Orphan Annie eye | - | Papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| Owl eye | CMV | CMV |
| Pappenheimer body | Ferritin | Sideroblastic anemia |
| Pelger-Huet cell | - | Myelodysplasia |
| Pick body | Tau protein | Frontotemporal dementia |
| Psammoma body | Calcium | Tumor |
| Reinke crystal | - | Leydig cell tumor |
| Russell body | Immunoglobulin | Multiple myeloma |
| Schiller-Duval body | - | Yolk sac tumor |
| Zebra body | Sphingolipid | Lysosomal storage diseases (LSD) |
Psammoma Body
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Prolactinoma
- Serous cystadenocarcinoma
- Meningioma
- Mesothelioma
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Stain Positive Diseases
- α1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Fungal infection
- Glycogen storage diseases (GSD)
- Nodular glomerulosclerosis
- Whipple disease
Types of Giant Cells
- Foreign-body giant cells
- Langhans giant cells
- Touton giant cells
- Giant-cell arteritis
Differential Diagnoses of Pagetoid Cells
- Paget's disease
- Extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD)
- Bowen's disease
- Melanoma
- Sebaceous carcinoma
Laboratory Tests
| Test | Target | Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Acidified glycerol lysis test | Spherocytes | Hereditary spherocytosis |
| Cold agglutinin test | Anti-RBC IgM | CLL Mycoplasma HCV & EBV & CMV |
| Coombs test | Anti-RBC | Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AHA) |
| Congo red stain | Amyloid | Amyloidosis |
| Cyanide-nitroprusside test | Disulfide bond | Cystinuria |
| Dihydrorhodamine test | NADPH oxidase | Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) |
| EMA binding test | Membrane skeleton | Hereditary spherocytosis |
| Fluorescent spot test | G6PD | G6PD deficiency |
| Hydrogen breath test | Lactase | Lactose intolerance |
| Gut bacteria | Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) | |
| Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) stain | Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) | AML & CML |
| Methylene blue reduction stain | G6PD | G6PD deficiency |
| Nitroblue tetrazolium test | NADPH oxidase | Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) |
| Osmotic fragility test | Spherocytes | Hereditary spherocytosis |
| Prussian blue stain | Iron | Hemochromatosis Sideroblastic anemia |
| Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) stain | Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) | Hairy cell leukemia |
| Warm agglutinin test | Anti-RBC IgG | CLL & SLE |
Pathological Grading of Neoplasm
| Grade | Hyperplasia | Atypia | Invasion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | + | - | - |
| Dysplastic | + | + | - |
| Malignant | + | + | + |
Pathological Features of Dysplasia
- Hypercellularity
- Loss of polarity
- Increased nucleus/cytoplasm (N/C) ratio
- Hyperchromatic nuclei
- Pleomorphic nuclei
- Prominent nucleoli
- Increased mitosis
Types of Giant Cells
- Foreign-body giant cells
- Langhan giant cells
- Touton giant cells