Digestive System
Treatment of Diffuse Esophageal Spasm (DES)
- Ca channel blockers :: -Dipines
- Reuptake inhibitors :: TCAs
- Nitrates :: Nitroglycerin & Isosorbide
Treatment of Esophageal Varices
- Somatostatin analogs
- Vasopressin
- β antagonists :: Propranolol
- Nitrates :: Nitroglycerin & Isosorbide
- Balloon tamponade
- Endoscopy
- Endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL)
- Endoscopic sclerotherapy (ES)
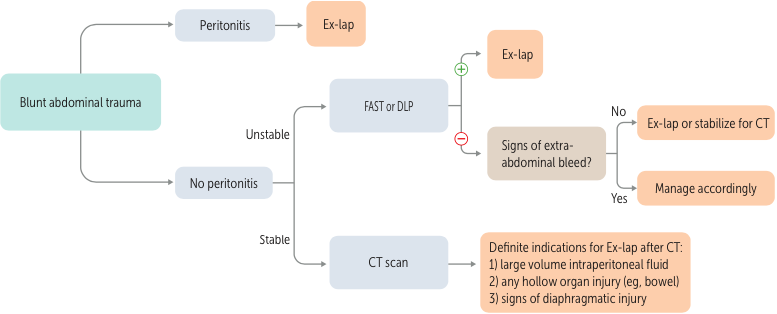
Management of Abdominal Trauma
| Condition | Management |
|---|---|
| Blunt trauma | Focused assessment with sonography in trauma (FAST) |
| Stable blunt trauma | Abdominal CT |
| Unstable blunt trauma | Diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL) |
| Known etiology | Exploratory laparotomy |
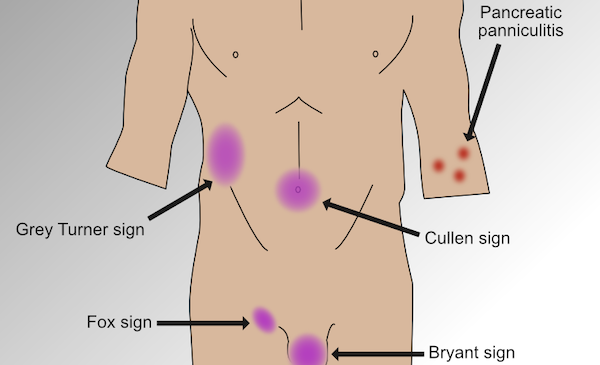
Signs of Retroperitoneal Hemorrhage
- Cullen sign
- Grey Turner sign
- Fox sign
- Bryant sign
Etiology of Gastritis
- Achlorhydria
- Alcohol
- Autoimmune gastritis
- Biliary reflux
- Brain injury → Cushing ulcer
- Burns → Curling ulcer
- Drugs
- NSAIDs
- Corticosteroids
- Ischemia
- Smoking
- Stress
- Helicobacter pylori
Brochardt Triad of Gastric Volvulus
- Intermittent epigastric pain and distention
- Inability to vomit
- Difficult passage of nasogastric (NG) tube
Medications for PUD
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| H-K pump blockers [Proton pump inhibitors (PPI)] | -Prazoles |
| H2 antagonists | Cimetidine Ranitidine Famotidine Nizatidine |
| PGE1 agonists | Misoprostol |
| Antacids | Aluminum hydroxide Calcium carbonate Magnesium hydroxide |
| Antimicrobials | Amoxicillin / Metronidazole Macrolides |
| - | Bismuth |
| - | Sucralfate |
Presentation of Gastric Adenocarcinoma
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Leser-Trélat sign
- Virchow node
- Sister Mary Joseph nodule
- Krukenberg tumor
- Blumer shelf
Types of Gastrectomy
- Local [Wedge] resection
- Sleeve gastrectomy
- Proximal gastrectomy
- Segmental [Pylorus-preserving] gastrectomy
- Distal gastrectomy
- Total gastrectomy
Gastric Reconstruction
Proximal Gastrectomy
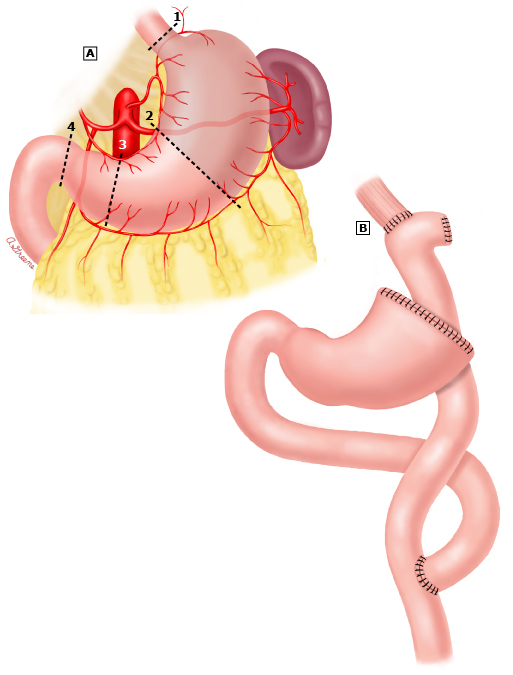
Segmental Gastrectomy
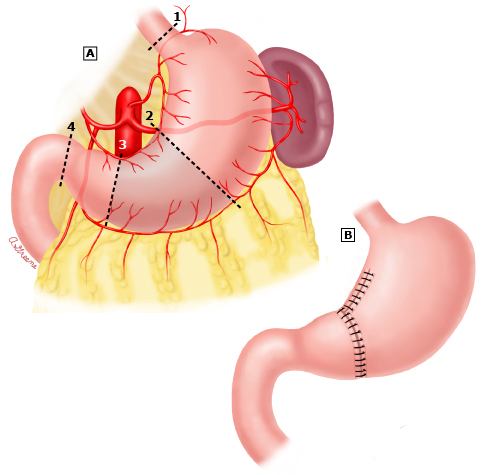
Distal Gastrectomy
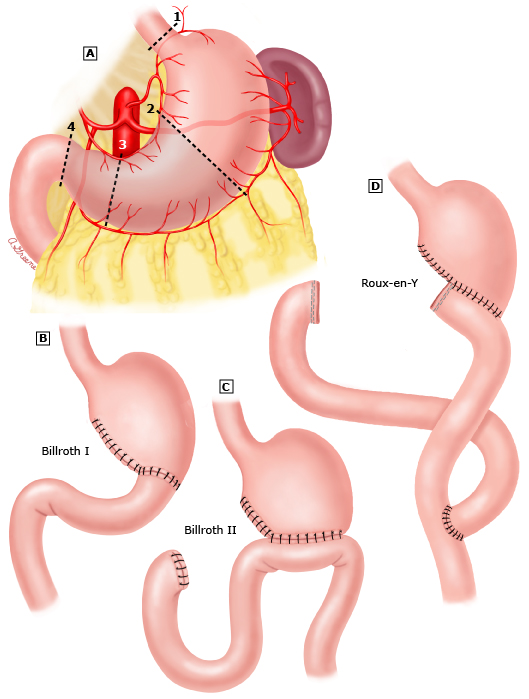
Total Gastrectomy
Complications of Gastrectomy
- Afferent & Efferent loop syndrome
- Internal hernia
- Marginal ulcer
- Dumping syndrome
- Early dumping syndrome
- Late dumping syndrome
- Postvagotomy diarrhea
- Alkaline gastritis
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Iron deficiency
Types of Bariatric Surgery
- Vertical banded gastroplasty (VBG)
- Laparoscopic adjustable gastric band (LAGB)
- Sleeve gastrectomy
- Biliopancreatic diversion
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB)
Types of Hernia
| Hernia | IL | Triangle | IIR | EIR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indirect inguinal hernia | Above | - | + | + |
| Direct inguinal hernia | Above | Inguinal | - | + |
| Femoral hernia | Below | Femoral | - | - |
- Inguinal ligament (IL)
- Internal inguinal ring (IIR)
- External inguinal ring (EIR)
Presentation of Appendicitis {PROM}
- Psoas sign
- Rovsing sign
- Obturator sign
- McBurney's point
Etiology of Nausea and Vomiting
- Gastroparesis
- Motion sickness
- Morning sickness
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
- Postoperation
Prokinetics
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| D2 antagonists | Metoclopramide Prochlorperazine Domperidone Droperidol |
| 5-HT4 agonists | Cisapride Mosapride |
| Stimulants | Macrolides |
Antiemetics
| Mechanism | Medication | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| M antagonists | Scopolamine | Motion sickness |
| D2 antagonists | Metoclopramide Prochlorperazine Domperidone Droperidol | Postoperation Chemotherapy |
| 5-HT3 antagonists | -Setrons | Postoperation Chemotherapy |
| H1 antagonists | 1° Antihistamines | Motion sickness Morning sickness |
| Neurokinin antagonists | Aprepitant | Chemotherapy |
| Cannabinoid agonists | Dronabinol | Chemotherapy |
| - | Corticosteroids | Chemotherapy |
Laxatives {SHELB}
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| 5-HT4 agonists | Cisapride Mosapride |
| Stimulants | Senna Bisacodyl |
| Hyperosmotics | Magnesium Polyethylene glycol Lactulose Enema |
| Emollients | Docusate |
| Lubricants | Mineral oil |
| Bulk-formers | Psyllium |
Etiology of Diarrhea
- Osmotic
- Secretory
- Exudative
- Infectious
- Inflammatory
- Dysmotility
Malabsorption Syndromes
- Pancreatic insufficiency
- Celiac disease
- Tropical sprue
- Whipple disease
Pathogens of Infectious Diarrhea
Watery {GBS-CAVERN}
- Giardia lamblia
- Bacillus cereus
- Staphylococcus aureus: heat-stable
- Clostridium difficile
- Cryptosporidium
- Adenovirus
- Vibrio cholerae
- ETEC & EPEC
- Rotavirus
- Norovirus
Bloody {SYCE}
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Yersinia enterocolitica
- Campylobacter
- EHEC & EIEC
- Entamoeba histolytica
Indications for Antibiotic Treatment of Diarrhea
- Pathogens w/o shiga toxin
- Pathogens w/ low infectious dose
- Immunodeficiency
- Hemodynamic instability
Rome Criteria for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Recurrent abdominal discomfort
- Relief a/w defecation
- Onset a/w frequency of stool
- Onset a/w appearance of stool
Etiology of Hematochezia
Painless
- Allergic proctocolitis
- Meckel diverticulum
- Diverticulosis
- Angiodysplasia
- Hemorrhoids
- Malignancy
Painful
- Intussusception
- Anal fissures
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Infectious colitis
- Diverticulitis
- Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
- Ischemic colitis
Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
| Crohn Disease | Ulcerative Colitis | |
|---|---|---|
| Involvement | Ileum & Colon | Colon & Rectum |
| Pattern | Skip | Contiguous |
| Depth | Transmural | Mucosal Submucosal |
| Radiography | String sign | Lead pipe |
| Colonoscopy | Cobblestones | Pseudopolyps |
| Histology | Granuloma | Crypt abscess |
| Immunology | Th1 | Th2 |
| Autoantibody | ASCA | Anti-MPO [p-ANCA] |
| Risk of colorectal cancer | ↑ | ↑↑ |
Grading of Hemorrhoids
| Grade | Proplase | Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - |
| 2 | + | Spontaneous |
| 3 | + | Manual |
| 4 | + | Irreducible |
Triad of Chronic Anal Fissures
- Sentinel pile
- Hypertrophied papilla
- Ulcer with scarred edges
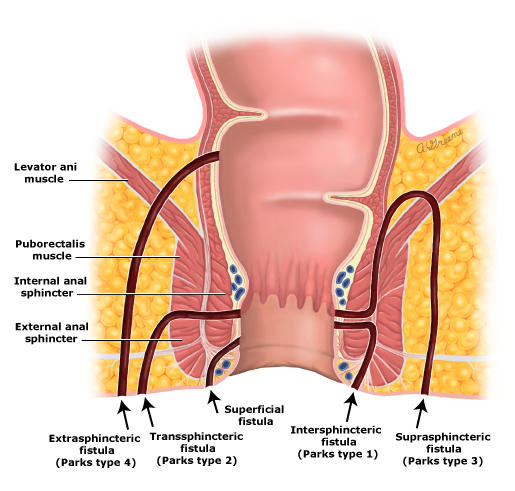
Park Classification of Anal Fistulas
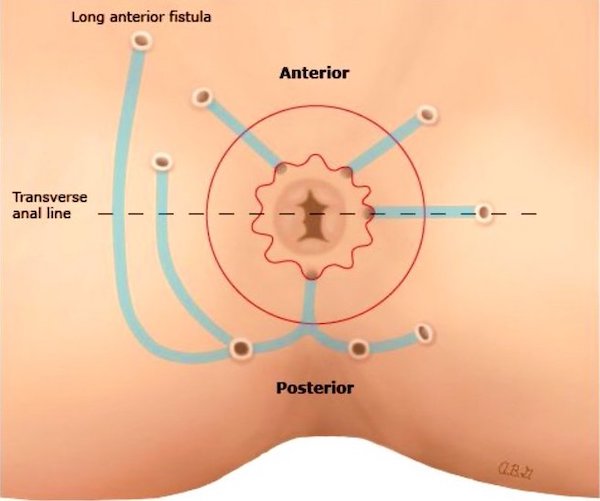
Goodsall Rule for Anal Fistulas
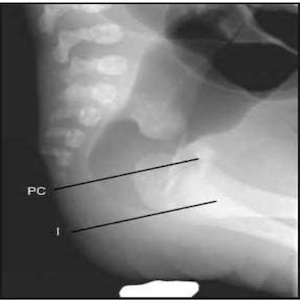
Anorectal Malformation
- Pubococcygeal (PC) line
- Ischial (I) line
Etiology of Ascites
| SAAG < 1.1 | SAAG > 1.1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Ascites TP < 2.5 | Nephrosis | Cirrhosis |
| Ascites TP > 2.5 | Cancer Infection | Right heart failure Budd-Chiari syndrome |
- Serum-Ascites albumin gradient (SAAG)
- Total protein (TP)
Child-Pugh Score for Cirrhosis {ABATE}
| Score | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ascites | Grade 0 | Grade 1 & 2 | Grade 3 & 4 |
| Bilirubin | < 2 | 2 ~ 3 | > 3 |
| Albumin | > 3.5 | 2.8 ~ 3.5 | < 2.8 |
| Time :: prothrombin [INR] | < 1.7 | 1.7 ~ 2.3 | > 2.3 |
| Encephalopathy | Grade 0 | Grade 1 & 2 | Grade 3 & 4 |
- Class A: 5 ~ 6
- Class B: 7 ~ 9
- Class C: 10 ~ 15
Complications of Cirrhosis
- Jaundice
- Spider angioma
- Palmar erythema
- Varices
- Esophageal varices
- Caput medusae
- Hemorrhoid
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- Hepatorenal syndrome
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
- Coagulopathy
Triad of Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- Pain :: RUQ
- Ascites
- Hepatomegaly
Types of Portosystemic Shunts for Portal Hypertension
| Shunt | Portal | System |
|---|---|---|
| Splenorenal [Warren] shunt | Splenic vein | Renal vein |
| Mesocaval H graft | SMV | IVC |
| Portacaval H graft | Portal vein | IVC |
| End-to-side portacaval anastomosis | Portal vein | IVC |
| Side-to-side portacaval anastomosis | Portal vein | IVC |
| Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) | Portal vein | Hepatic vein |
Etiology of Hepatitis
- Ischemic hepatitis
- Congestive hepatopathy
- Viral hepatitis
- Malignant infiltration
- Drug-induced liver injury (DILI)
- α1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Alcoholic hepatitis
Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
| Resectable | VI/EM | Child-Pugh Score | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | - | ≤ B | Hepatectomy Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) |
| + | - | C | Liver transplantation |
| - | - | ≤ B | Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) |
| - | + | ≤ B | Chemotherapy |
| - | ± | C | Supportive care |
- Vascular invasion (VI)
- Extrahepatic metastasis (EM)
%20Staging.gif)
Model for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD)
| Parameter | (0.957 × ln Cr + 0.378 × ln Bilirubin + 1.120 × ln INR) × 10 |
|---|---|
| Cr | Serum creatinine |
| Bilirubin | Serum bilirubin |
| INR | Serum INR |
Makuuchi Criteria for Hepatectomy
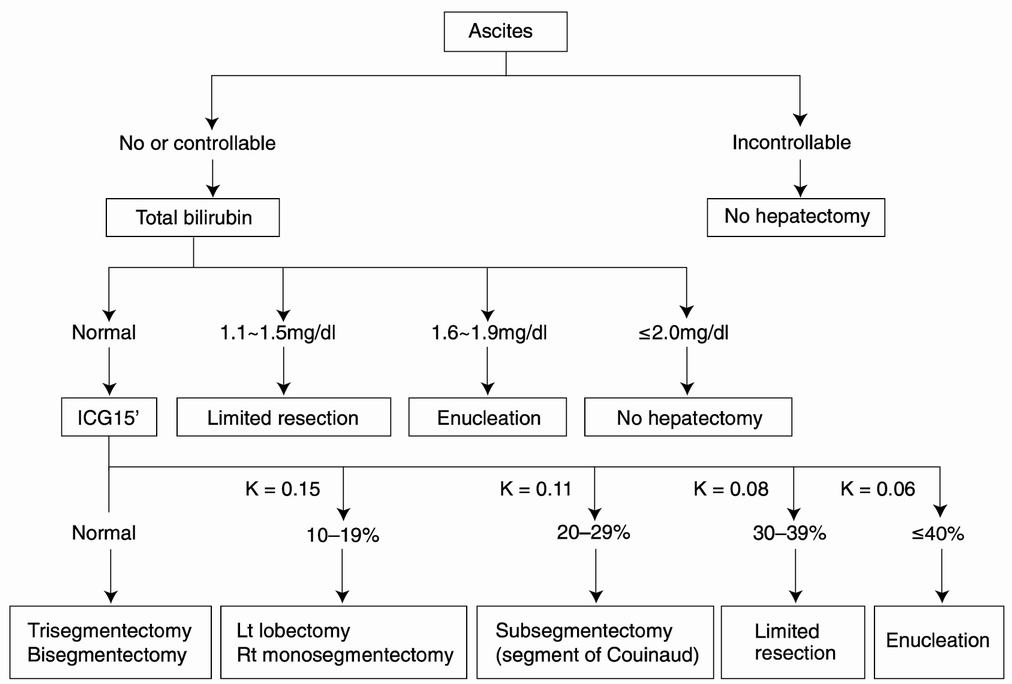
Criteria for Liver Transplantation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Milan Criteria
- Resectable tumor(s):
- 1 tumor: < 5 cm
- ≤ 3 tumors: each < 3 cm
- No vascular invasion
- No extrahepatic metastasis
UCSF Criteria
- Resectable tumor(s):
- 1 tumor: < 6.5 cm
- ≤ 3 tumors: each < 4.5 cm & total < 8 cm
- No vascular invasion
- No extrahepatic metastasis
Etiology of Hyperbilirubinemia
| Indirect | Direct | Mixed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum indirect bilirubin | ↑ | - | ↑ |
| Serum direct bilirubin | - | ↑ | ↑ |
| Urine bilirubin | - | ↑ | ↑ |
| Urine urobilinogen | ↑ | ↓ | - |
| Tea-colored urine | - | + | + |
| Clay-colored stool | - | + | + |
- Indirect
- Gilbert syndrome
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome
- Neonatal jaundice
- Extravascular hemolysis
- Direct
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome
- Rotor syndrome
- Obstructive jaundice
- Mixed
- Hepatitis
- Cirrhosis
Comparison Between Biliary Diseases
| Disease | Pain | Fever | Bil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cholelithiasis | ± | - | - |
| Cholecystitis | + | + | - |
| Choledocholithiasis | ± | - | ↑ |
| Cholangitis | + | + | ↑ |
Charcot Triad of Cholangitis
- Pain :: RUQ
- Fever
- Jaundice
Pathogens of Biliary Tract Infection (BTI)
- Enterococcus
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Anaerobes
Etiology of Acute Pancreatitis
- Gallstones
- Alcohol
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Drugs
Indications for Whipple Procedure
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Ampullary carcinoma
- Duodenal neoplasm
- Chronic pancreatitis
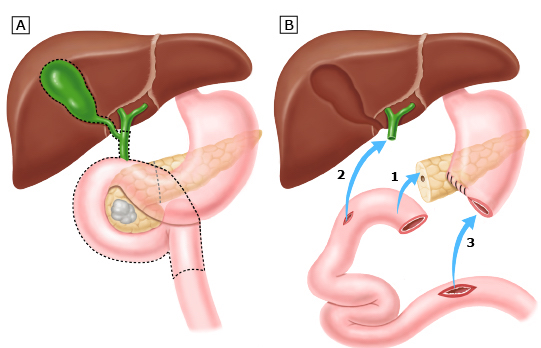
Whipple Procedure
- Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Gastrojejunostomy
- Pancreaticojejunostomy
- Cholangiojejunostomy
- ± Roux-en-Y reconstruction
Presentation of VIPoma {WDHA}
- Watery diarrhea
- Hypokalemia
- Achlorhydria