Hematopoietic System
Etiology of Target Cells {HALT}
- HbC disease
- Asplenia
- Liver disease
- Thalassemia
Etiology of Anemia
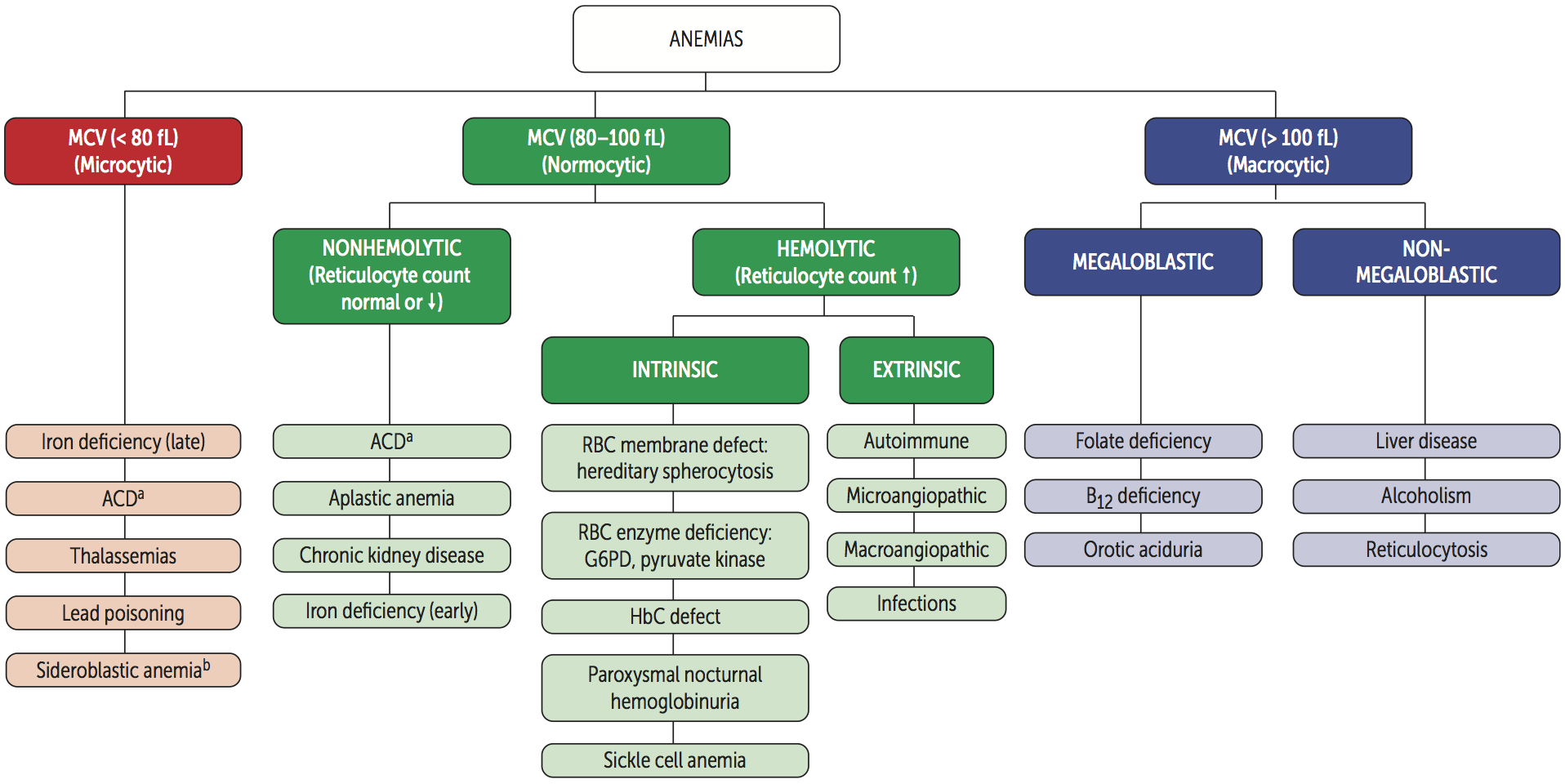
Microcytic Anemia {TAILS}
| Anemia | Fe | Ferritin | Transferrin [TIBC] | Saturation = Fe ÷ TIBC | Defect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thalassemia | - | - | - | - | Hemoglobin |
| Anemia of chronic disease (ACD) | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | - | Fe |
| Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | Fe |
| Lead poisoning | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | Heme |
| Sideroblastic anemia | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ | Heme |
Normocytic Anemia
Non-hemolytic Anemia
- Aplastic anemia
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Hemolytic Anemia
| Intravascular | Extravascular | |
|---|---|---|
| Peripheral smear | Schistocyte | Spherocyte |
| Haptoglobin | ↓ | - |
| Hemoglobin | ↑ | - |
| Hematuria | + | - |
| Indirect bilirubin | - | ↑ |
| Direct bilirubin | - | - |
| Urine bilirubin | - | - |
| Urine urobilinogen | - | ↑ |
| LDH | ↑ | ↑ |
| Jaundice | - | + |
Intravascular Hemolytic Anemia {TIMP}
- Transfusion
- Infusion
- Macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
- HELLP syndrome
- Paroxysmal nocturnal hematuria (PNH)
Extravascular Hemolytic Anemia {PHAGES}
- Pyruvate kinase deficiency
- HbC disease
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AHA)
- G6PD deficiency
- Elliptocytosis
- Sickle cell disease (SCD)
Macrocytic Anemia
Megaloblastic
- Folate deficiency
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Orotic aciduria
- Fanconi anemia
Non-megaloblastic
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia
- Alcoholism
- Reticulocytosis
Etiology of Elevated RDW
- Iron deficiency anemia (IDA)
- Folate deficiency anemia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia
- Mixed anemia
Comparison Between Thalassemia and IDA
| Thalassemia | IDA | |
|---|---|---|
| Mentzer index = MCV ÷ RBC | < 13 | > 13 |
| RDW | - | ↑ |
| Iron profile | Normal | Abnormal |
| Blood smear | Target cells | - |
Etiology of Aplastic Anemia
- Fanconi anemia
- Virus
- Parvovirus B19
- EBV
- CMV
- HIV
- Hepatitis virus
- Drugs
- Carbamazepine
- Methimazole
- Propylthiouracil
- NSAIDs
- Chloramphenicol
- Toxins :: Benzene
- Radiation
Presentation of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
- Vaso-occlusive crisis (VOC)
- Acute chest syndrome
- Mesenteric ischemia
- Ischemic stroke
- Hemolysis :: extravascular
- Splenic sequestration
- Aplastic crisis
- Avascular necrosis
- Osteomyelitis
- Dactylitis
- Priapism
Triggers of Vaso-occlusive Crisis (VOC) in Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
- Dehydration
- Infection
- Hypoxia
- Cold temperatures
Management of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
- Immunizations
- Penicillin prophylaxis
- Folate supplementation
- Transfusion
- Hemapheresis
- Hydroxyurea
- Bone marrow transplantation
Treatment of Polycythemia
- Phlebotomy
- Antiplatelets :: Aspirin
- Cytoreductive agents
- Hydroxyurea
- Interferon
- Busulfan
Abnormal Hemoglobin Variants
| α-Globin | Disease | α-Globin Defect | Disease | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Globin | α2β2 [HbA] | - | β4 [HbH] | α-thalassemia :: 3 deletion |
| γ-Globin | α2γ2 [HbF] | β-thalassemia major | γ4 [Hb Barts] | α-thalassemia :: 4 deletion |
| δ-Globin | α2δ2 [HbA2] | β-thalassemia minor | - | - |
| s-Globin | α2s2 [HbS] | Sickle cell disease | - | - |
| c-Globin | α2c2 [HbC] | HbC disease | - | - |
Heme Synthesis Disorders
- Lead poisoning
- Sideroblastic anemia
- Alcoholism
- ALA synthase deficiency
- Vitamin B6 deficiency
- Copper deficiency
- Porphyria
Types of Porphyria
- Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)
- Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)
- Erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP)
Presentation of Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) {5P}
- Pain :: abdomen
- Port wine-colored urine
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Psychological disturbances
- Precipitation
- Starvation
- Alcohol
- Cytochrome P-450 (CYP450) inducers
Types of Transfusion Reactions
| Type | Causes | Onset |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic | Anti-plasma proteins IgE Anti-IgA IgE | Minutes ~ Hours |
| Hemolytic (HTR) | Anti-ABO Anti-Rh | Minutes ~ Days |
| Febrile non-hemolytic (FNHTR) | Anti-WBC | Hours |
Classificaiton of Leukemia
Myeloid Leukemia
| Tumor | Mutation | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| AML | t(15;17) | PML/RARA |
| t(8;21) | RUNX1/RUNX1T1 | |
| t(16;16) | CBFB/MYH11 | |
| - | NPM1 | |
| - | CEBPA | |
| - | FLT3 | |
| CML | t(9;22) | BCR/ABL1 |
- Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
Lymphoid Leukemia
| Tumor | Mutation | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | t(12;21) | ETV6/RUNX1 |
| t(1;19) | TCF3/PBX1 | |
| t(9;22) | BCR/ABL1 | |
| t(4;11) | MLL/AF4 | |
| Hyperdiploidy > 50 | - | |
| Hypodiploidy < 44 | - | |
| CLL | - | - |
| HCL | - | - |
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- Hairy cell leukemia (HCL)
Workup of Leukemia
- Peripheral blood smear
- Bone marrow smear
- Cytochemistry
- Immunophenotyping
- Karyotyping
- Genotyping
Treatment of Leukemia
| Leukemia | Treatment |
|---|---|
| AML | Anthracyclines Cytarabine All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) |
| CML | Imatinib |
| ALL | - |
| CLL | Fludarabine Cyclophosphamide Rituximab |
| HCL | Cladribine |
Classificaiton of Lymphoma
T-cell Lymphoma
| Tumor | Mutation | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| Adult T-cell lymphoma | - | - |
| Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma | - | - |
B-cell Lymphoma
| Tumor | Mutation | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| Hodgkin lymphoma | - | - |
| Burkitt lymphoma | t(8;14) | C-MYC |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) | - | - |
| Mantle cell lymphoma | t(11;14) | Cyclin D (CCND) |
| Marginal zone lymphoma MALT lymphoma (MALToma) | - | - |
| Follicular lymphoma | t(14;18) | BCL2 |
B Symptoms of Lymphoma
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
Treatment of Hodgkin Lymphoma {ABVD}
- Doxorubicin [Adriamycin]
- Bleomycin
- Vinblastine
- Dacarbazine
Treatment of B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma {R-CHOP}
- Rituximab
- Cyclophosphamide
- Doxorubicin [Hydroxydaunorubicin]
- Vincristine [Oncovin]
- Prednisolone
Causes of Monoclonal Spike [M Spike]
- Multiple myeloma
- Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
- Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
- AL amyloidosis
Presentation of Multiple Myeloma {CRAB}
- Hypercalcemia
- Renal failure
- Rouleaux formation
- Russell body
- Anemia
- Amyloidosis :: primary
- Back pain
- Bone lesions
- Bence-Jones protein
Diagnostic Tests for Multiple Myeloma
- Protein electrophoresis
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Skeletal survey
Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma
- Histology of bone marrow
- Clonal bone marrow plasma cells > 10%
- Plasmacytoma
- Evidence of end-organ damages {CRAB}
- Hypercalcemia
- Renal failure
- Anemia
- Bone lesions
- Evidence of inevitable end-organ damages
- Free light chain (FLC) ratio > 100
- Clonal bone marrow plasma cell > 60%
- Bone lesions on MRI > 1
Presentation of Hemophagocytic Lymphohisticytosis (HLH)
- Fever
- ↑ Ferritin
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Hemophagocytosis
- ↓ NK cell activity
- Pancytopenia
- Rashes
- Splenomegaly
Myeloproliferative Disorders
| Tumors | Genetics | RBC | WBC | PLT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polycythemia vera | JAK2 | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) | t(9;22) | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Essential thrombocytosis | JAK2 | - | - | ↑ |
| Myelofibrosis | JAK2 | ↓ | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ |
Virchow Triad for Thrombosis {SHE}
| Cause | Effect |
|---|---|
| Stasis | VTE |
| Hypercoagulability | ATE / VTE |
| Endothelial injury | ATE |
Etiology of Hypocoagulability
| Etiology | Mechanism | PLT | BT | PT | PTT | Clots |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) | - | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | + |
| Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) | ↓ ADAMTS13 | ↓ | ↑ | - | - | + |
| Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) | ↓ ADAMTS13 Shiga-like toxin | ↓ | ↑ | - | - | + |
| HELLP syndrome | - | ↓ | ↑ | - | - | - |
| Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) | Anti-Gp1b Anti-Gp2b/3a | ↓ | ↑ | - | - | - |
| Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) | Anti-platelet factor 4 (Anti-PF4) | ↓ | ↑ | - | - | + |
| Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) | Anti-cardiolipin Anti-β2-glycoprotein I Lupus anticoagulant | - | - | - | ↑ | + |
| Von Willebrand disease (VWD) | ↓ vWF | - | ↑ | - | ↑ | - |
| Bernard-Soulier disease (BSD) | ↓ Gp1b | - | ↑ | - | - | - |
| Glanzmann disease | ↓ Gp2b/3a | - | ↑ | - | - | - |
| Hemophilia A & B & C | ↓ Factor 8 & 9 & 11 | - | - | - | ↑ | - |
| Vitamin K deficiency | ↓ Factor 2 & 7 & 9 & 10 | - | - | ↑ | ↑ | - |
| Cirrhosis | ↓ Thrombopoietin (TPO) ↓ Factors | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ | - | - |
Etiology of Hypercoagulability
| Etiology | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Homocysteinemia | ↑ Factor 7 |
| Factor 5 Leiden mutation | ↑ Factor 5 |
| Prothrombin gene mutation | ↑ Factor 2 |
| Antithrombin deficiency | ↓ Antithrombin |
| Protein C/S deficiency | ↓ Protein C/S |
| Nephrosis | ↓ Protein C/S |
| Pregnancy | ↑ Factor 1 |
Antiplatelets
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| Gp2b/3a inhibitors | Abciximab Eptifibatide Tirofiban |
| ADP antagonists | Clopidogrel Prasugrel Ticagrelor Ticlopidine |
| PDE inhibitors | Dipyridamole Cilostazol |
| COX inhibitors | NSAIDs |
Anticoagulants
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| VKOR inhibitors | Warfarin Coumadin |
| Antithrombin inducers | Unfractionated heparin (UFH) |
| Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH): Enoxaparin Dalteparin | |
| Fondaparinux | |
| Factor 10a inhibitors | Apixaban Edoxaban Rivaroxaban |
| Factor 2a inhibitors | Hirudin Bivalirudin Argatroban Dabigatran |
| Tissue plasminogen activators (tPAs) | Urokinase Streptokinase Alteplase Reteplase Tenecteplase |
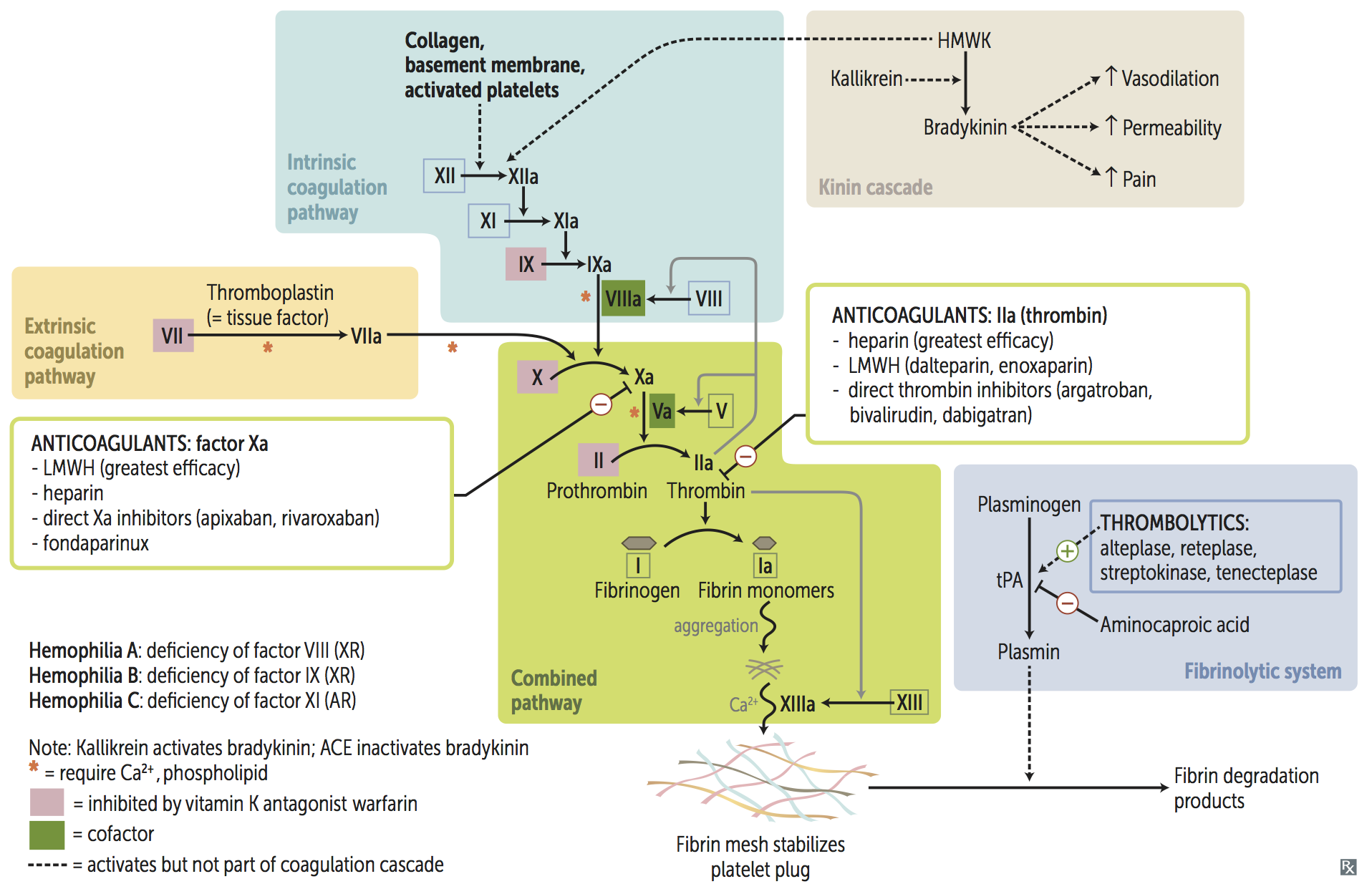
Heparin Variants
| UFH | LMWH | |
|---|---|---|
| Bioavailability | - | ↑ |
| Half-life | - | ↑ |
| Specificity to Factor 10a | - | ↑ |
| Monitor | PTT | - |
| Side Effect | HIT & Osteoporosis | - |
| Antidote | Protamine sulfate | - |
Goal INR
| Condition | INR |
|---|---|
| Venous thromboembolism (VTE) | 2.0 ~ 3.0 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 2.0 ~ 3.0 |
| Bioprosthetic valve | 2.0 ~ 3.0 |
| Mechanical valve | 2.5 ~ 3.5 |
Management of Supratherapeutic INR
| INR | Management |
|---|---|
| < 4.5 | Hold warfarin |
| 4.5 ~ 10 | Hold warfarin Low-dose oral vitamin K |
| > 10 | Hold warfarin High-dose oral vitamin K |
| Bleeding | Hold warfarin High-dose IV viatamin K FFP / PCC |
Etiology of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
| Mnemonic | Cause |
|---|---|
| S | Sepsis :: GNB |
| T | Trauma |
| O | Obstetric complications |
| P | Pancreatitis :: acute |
| Making | Malignancy |
| New | Nephrotic symdrome |
| Thrombi | Transfusion |
Pentad of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
- Renal symptoms
- Anemia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Neurologic symptoms
- Fever
Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
- Plasmapheresis
- Immunosuppression
- Corticosteroids
- Rituximab
Triad of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
- Renal symptoms
- Anemia
- Thrombocytopenia
Treatment of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
- Immunosuppression
- Corticosteroids
- Rituximab
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
- Splenectomy
Indications for Thrombolytics
- ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
- Duration < 12 ~ 24 hours
- Door-to-bolloon > 2 hours
- Ischemic stroke
- Duration < 3 ~ 4.5 hours
- BP < 185/110 mmHg
- Pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Hemodynamic instability
Contraindications to Thrombolytics
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Internal bleeding
- Bleeding tendency
Plasma Products
- Fresh frozen plasma (FFP)
- Prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC)
- Cryoprecipitate
- Factor concentrate
Indications for Plasma Products
| Product | Indications |
|---|---|
| FFP / PCC | Warfarin toxicity Factor 10a inhibitors toxicity |
| Cryoprecipitate | tPA toxicity Fibrinogen deficiency Hemophilia A Von Willebrand disease (VWD) Uremic bleeding |
| Factor concentrate | Factor deficiency |
Antifibrinolytics
- Tranexamic acid
- Aminocaproic acid