Special Senses
Abnormal Fundoscopic Findings
| Finding | Diseases |
|---|---|
| Cherry-red spots | Retinal artery occlusion Lysosomal storage diseases (LSD) |
| Cotton-wool spots | Diabetic retinopathy Hypertensive retinopathy Retinal vein occlusion CMV retinitis |
| Drusen | Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) |
| Optic nerve cupping | Open-angle glaucoma |
Etiology of Ophthalmoplegia & Nystagmus
| Lesion | Presention | Etiology |
|---|---|---|
| Inner ear | Peripheral vertigo | Vestibular disorders |
| CN VIII | Bruns nystagmus | Cerebellopontine angle tumors |
| Superior colliculus | Vertical gaze palsy | Parinaud syndrome |
| Frontal eye fields (FEF) Paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF) | Horizontal gaze palsy | - |
| Medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) | Internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) | Multiple sclerosis |
| CN III | Down-and-out gaze | Cavernous sinus thrombosis Posterior communicating artery aneurysm Uncal herniation |
| Extraocular muscles | - | Myasthenic syndrome Thyroid ophthalmopathy |
| Mammillary body | - | Wernicke encephalopathy |
| - | - | Epilepsy Stroke Migraine Chiari malformation |
Presentation of Parinaud Syndrome
- Vertical gaze palsy
- Convergence-retraction nystagmus
- Light-near dissociation
- Collier sign
Etiology of Miosis
- Drug-induced
- ACh esterase inhibitors
- M agonists
- α2 agonists
- Opioids
- Cluster headaches
- Horner syndrome
Etiology of Mydriasis
- Drug-induced
- M antagonists
- NDRIs
- CN III damage
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis
- Posterior communicating artery aneurysm
- Uncal herniation
- ↑ Intracranial pressure (ICP)
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Cerebral edema
- ↑ Intraocular pressure (IOP)
Presentation of Glaucoma
- Headache
- Nausea ± vomiting
- Visual disturbances
- Non-reactive pupil
- Mydriasis
Medications for Glaucoma
| Mechanism | Medication |
|---|---|
| ACh esterase inhibitors | Organophosphate Sarin |
| M agonists | Carbachol Pilocarpine |
| α2 agonists | Brimonidine |
| β antagonists | Timolol |
| PGF2 agonists | Latanoprost |
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors | Acetazolamide |
Treatment of Dry Eye Disease (DED)
- Cyclosporine :: topical
- Lifitegrast :: topical
- Corticosteroids :: topical
- Pilocarpine
- Punctal occlusion
- Autologous serum tears
Abnormal Physical Examination Findings in Hearing Loss
| Hearing Loss | Rinne Test | Weber Test |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | AC > BC | Left = Right |
| Sensorineural | AC > BC | Lesion < Normal |
| Conductive | AC < BC | Lesion > Normal |
- Air conduction (AC)
- Bone conduction (BC)
Abnormal Audiographic Findigs
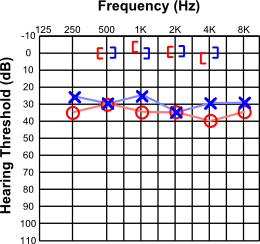
Conductive Hearing Loss
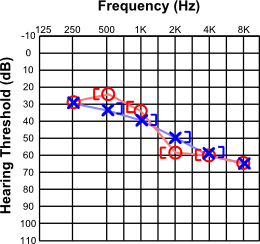
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
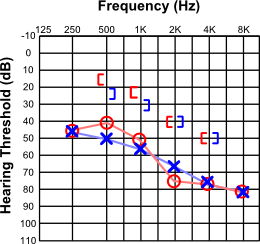
Mixed Hearing Loss
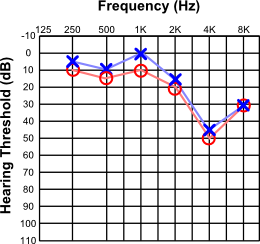
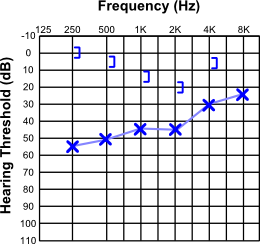
Noise-induced Hearing Loss
Presbycusis
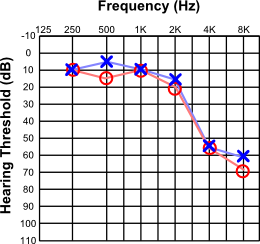
Meniere Disease
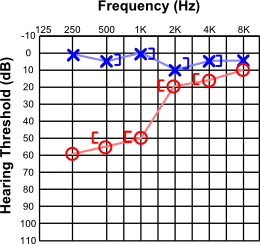
Osteosclerosis
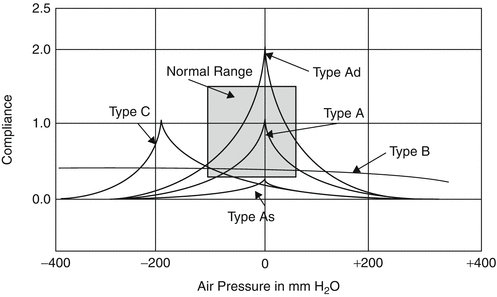
Abnormal Findings on Tympanometry
| Type | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A | Normal |
| Ad | Ossicular chain dislocation |
| As | Tympanosclerosis |
| B | Perforation |
| C | Eustachian tube dysfunction |
Etiology of Peripheral Vertigo
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)
- Labyrinthitis
- Labyrinthine concussion
- Meniere disease
- Vestibular neuritis
- Vestibular schwannoma
Pathogens of Otitis Externa
- Enterobacter
- Pseudomonas
Pathogens of Otitis Media {SHM}
- Streptococcus pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis
- Allergen avoidance
- Intranasal H1 antagonists
- Oral H1 antagonists
- Intranasal corticosteroids
Treatment of Nonallergic Rhinitis (NAR)
- Intranasal H1 antagonists
- Intranasal corticosteroids
Pathogens of Sinusitis {SHM}
- Streptococcus pneumonia
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Mucor and Rhizopus
Pathogens of Pharyngitis & Tonsillitis
- Group A streptococcus (GAS)
- Adenovirus
- HSV
- EBV
- CMV
- HIV
- Parainfluenza virus
- Influenza virus